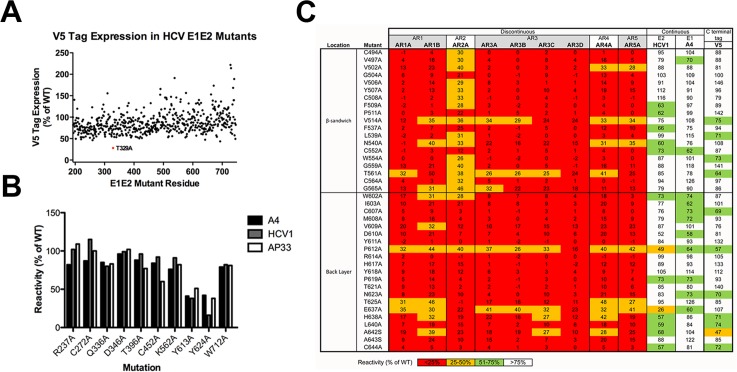
Fig 2. Identification of mutations that impair global folding.
(A) The V5 tag present at the C-terminus of 545 mutants was used as a marker of overall E1E2 expression. The expression of the V5 tag for each mutant was normalized to V5 expression on wild-type E1E2 (left). Only one mutation T329A (red dot) resulted in markedly decreased V5 expression. (B) The expression of the ten remaining mutants not present in the library was assessed using antibodies targeting continuous epitopes as controls. A4 targets E1, and HCV1 and AP33 are specific for distinct but overlapping epitopes from E2 aa 412–423. (C) Numerous mutations resulted in less than 50% binding (relative to wild-type) to the panel of conformation-dependent antibodies (AR1-5) when analyzed by flow cytometry. These mutants were predominantly located in the central Ig-like β sandwich or the back layer of E2. Binding of HCV1 and A4, which recognize linear epitopes of E2 and E1, respectively, were included along with V5 tag expression. Coloring corresponds to the reactivity to each E1E2 mutant with <25% red, 25–50% orange, 51–75% green, and >75% white.