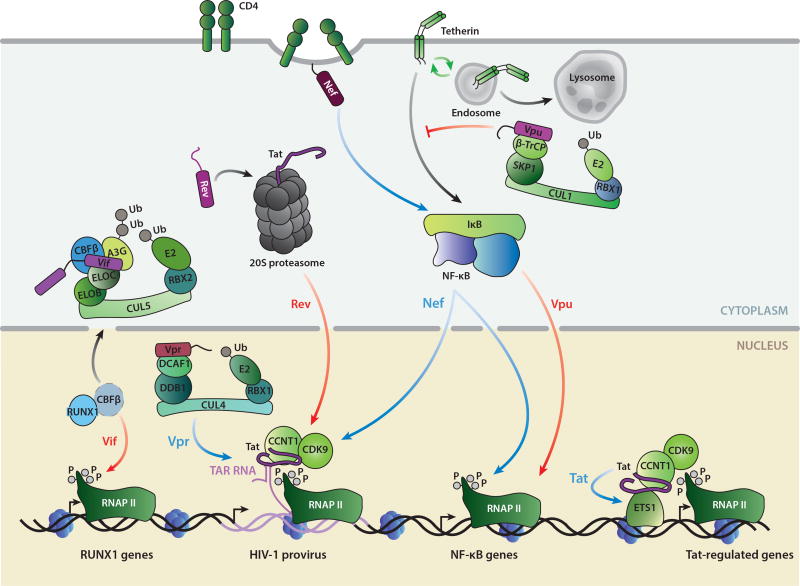
Figure 2.
Transcriptional effects of HIV-1 accessory and regulatory proteins. Tat directly deregulates multiple cellular genes through the ETS1 transcription factor. Rev-induced degradation of Tat through the 20S proteasome decreases HIV-1 transcription. Vif sequesters CBFβ from RUNX1 to decrease RUNX1-dependent transcription, including the A3G gene. Vpr DNA damage response activation and G2 arrest activate HIV-1 transcription. Membrane-bound Nef modulates signaling pathways through NF-κB to activate both viral and cellular transcription. Vpu inhibits tetherin signaling through NF-κB to decrease transcription at NF-κB target genes. Blue arrows indicate positive effects on transcription, whereas red arrows indicate inhibitory effects.