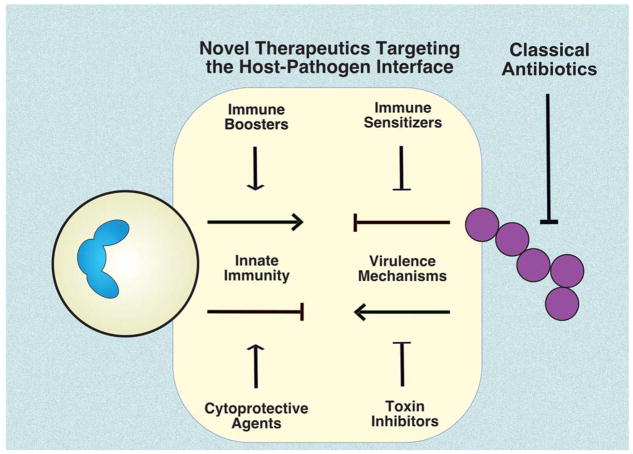
Figure 1. Potential for novel infectious disease therapeutics targeting the host-pathogen interface.
Classical antibiotics, drugs that kill or suppress the growth of pathogens, have been the cornerstones of infectious disease therapy for decades. However, continual evolution of antibiotic resistance has eroded their once reliable efficacy. Considering serious bacterial infection as a perturbation of the host-pathogen interaction, novel therapeutic drug classes are under evaluation. These drugs seek to inhibit bacterial toxins and immune resistance factors, or stimulate immune cell resilience and expression of antimicrobial effectors.