Fig. 8. A proposed model depicting the molecular mechanism by which AMPK regulates actin dynamics, MRTF-A nuclear translocation, and fibroblast activation.
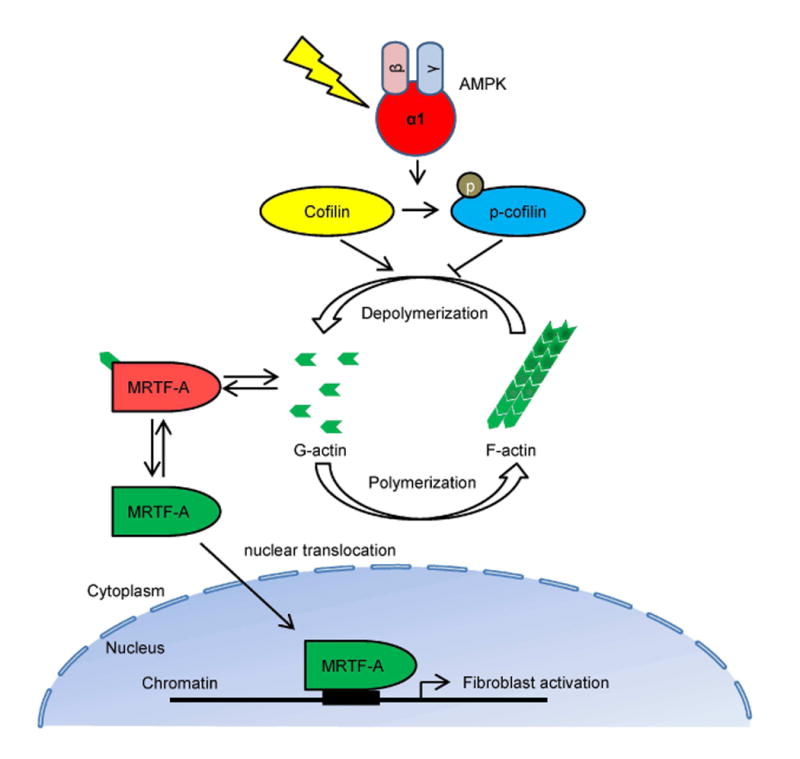
Under normal condition, cofilin severs and depolymerizes F-actin into G-actin, and cytoplasmic G-actin associates and retains MRTF-A in the cytoplasm. In response to injury, activated AMPK directly phosphorylates cofilin, which promotes G-actin to F-actin polymerization. Lower G-actin concentration results in releases of MRTF-A from binding to G-actin, which enters into the nucleus and induces fibroblast activation.
