Extended Data Figure 8. RHEB-induced conformational change in mTORC1.
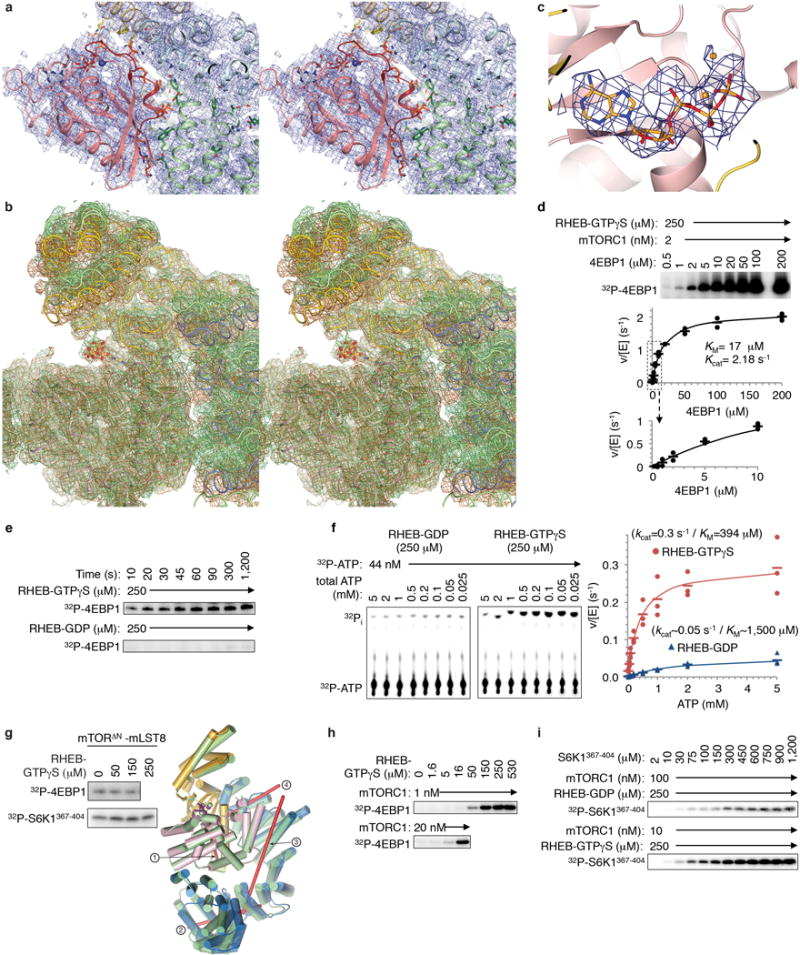
a, Stereo view of the cryo-EM density from the 3.4 Å RHEB-mTORC1 reconstruction, showing the RHEB-mTOR interface in the same orientation and coloring as in Figure 4c. The RHEB-interacting segments of mTOR are nα3 to nα7 of N-heat, mα2-mα4 of M-heat and fα2-fα3 of FAT. The majority of the contacts made by RHEB are from its switch I and switch II regions, with a small number of additional contacts to N-heat and M-heat contributed by the nearby segments of residues 5 to 7 and 106 to 111. b, Stereo view of cryo-EM density from RHEB-mTORC1 (sand) and the 3.0 Å apo-mTORC1 (green), with the two structures and maps superimposed on the C lobes as in Figure 5d. c, AMPPNP (orange) cryo-EM density of apo-mTORC1. d, Steady state kinetic analysis of mTORC1 phosphorylation of intact 4EBP1 in the presence of 250 μM RHEB-GTPγS. Reactions quantified by 32P incorporation and plotted as velocity over enzyme concentration (means as dashes and values from two independent experiments as filled circles). The KM and kcat values, calculated by non-linear regression fitting of the data, and simulated curves are also shown. Note that in contrast to the reaction in the absence of RHEB shown in Extended Data Figure 4e, the curve of reaction velocity versus 4EBP1 concentration obeys Michaelis-Menten kinetics. e, RHEB-GTPγS activation of 4EBP1 phosphorylation by mTORC1 under single-turnover conditions. A master mix of excess mTORC1 (500 nM) over 4EBP1 substrate (100 nM) was incubated with 250 μM RHEB-GTPγS or 250 μM RHEB-GDP in the standard kinase buffer on ice for 5 minutes. Reactions were started by the addition of a mixture of cold ATP (50 μM final) and [γ -32P] ATP (8 μCi per reaction time point). The reactions were done on ice to slow down the reaction. At indicated time points, an aliquot of the reaction was drawn, stopped, and analyzed as described in Methods. The experiment was repeated three times with very similar results. f, ATP steady-state kinetic parameters of ATP hydrolysis by mTORC1 in the presence of 250 μM RHEB-GDP (left, blue plot) or RHEB-GTPγS (right, red plot). Reactions quantified by 32P incorporation as in d. Graph shows means as dashes and values from three independent experiments with the indicated markers and colors. The steady-state kinetic constants of the RHEB-GDP containing reaction are approximate owing to the weak signal of these reactions. g, As expected, RHEB-GTPγS did not activate the truncated mTORΔN-mLST8 complex phosphorylating 4EBP1 or S6K1367–404 (10 μM both; mTORΔN at 20 and 30 nM, respectively) (left panel; experiments were repeated two times with very similar results). mTORΔN-mLST8 has an intermediate kcat of 0.66 s−1 (Extended Data Fig. 1b) compared to the 0.09 and 2.9 s−1 kcat values of apo-mTORC1 and RHEB-mTORC1, respectively (Fig. 5g). mTORΔN-mLST8 has a distinct FAT conformation likely due to the absence of N-heat. Right panel shows superposition of the FAT plus kinase domain portions of inactive apo-mTORC1 on the crystal structure of mTORΔN-mLST8 done by aligning their C lobes. Apo-mTORC1 is in green and mTORΔN is colored blue for FAT, yellow for N-lobe and pink for C-lobe. The rotation axes (red lines) are numbered according to the hinges of Figure 5c. Compared to the inactive to active transition, the comparison of the mTORΔN FAT conformation to that of the inactive state exhibits bigger changes around the major hinge with a rotation in the opposite direction and a different rotation axis far from the hinge axis (labeled “1”). The rotations around the two minor hinges are comparably modest although distinct, with the rotation axes nearly orthogonal to those of the inactive to active transition. h, Autoradiogram showing activation of mTORC1 phosphorylating 4EBP1 (10 μM) by RHEB-GTPγS, repeated three times. Gel quantification is shown in Figure 5b. i, Steady-state kinetic analysis of mTORC1 phosphorylating S6K1367–404 in presence of 250 μM RHEB-GDP (top row) or RHEB-GTPγS (bottom row). 32P incorporation data is plotted as velocity over enzyme concentration in Figure 5g (n=3).
