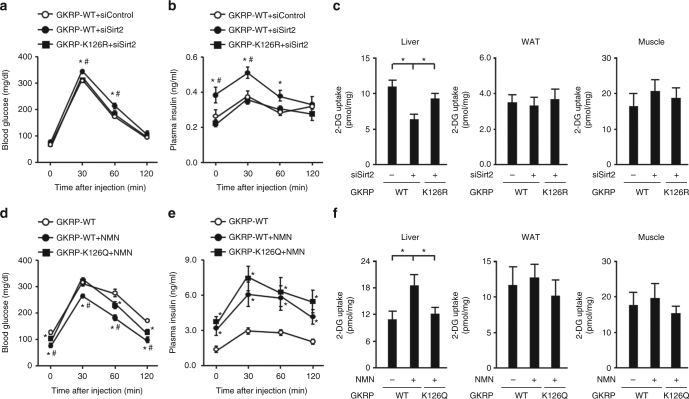
Fig. 6.
Deacetylation of K126 on GKRP plays an essential role in NAD+ /Sirt2-dependent hepatic glucose uptake. a–c Effect of adenovirus-mediated hepatic overexpression of GKRP-K126R or GKRP-wild-type (GKRP-WT) in hepatic Sirt2 knockdown mice on the levels of blood glucose (n = 5) (a), plasma insulin (n = 5) (b), and 2-deoxyglucose (2-DG) uptake in the liver, WAT, and skeletal muscle (n = 4) (c) after glucose administration (2 g/kg). d–f Effect of adenovirus-mediated hepatic overexpression of GKRP-K126Q or GKRP-WT in high-fat diet (HFD)-fed mice administered NMN on the levels of blood glucose (n = 5) (d), plasma insulin (n = 5) (e), and 2-DG uptake in the liver, WAT, and skeletal muscle (n = 4) (f) during glucose administration (1 g/kg). *P < 0.05; one-way ANOVA with the Fisher’s PLSD post-hoc test (c, f), *P < 0.05, vs. WT in (a, b, d, e), #P < 0.05, WT+siSirt2 vs. K126R+siSirt2 (a, b) or WT+NMN vs. K126Q+NMN (d, e); one-way ANOVA with the Fisher’s PLSD post-hoc test. Error bars show s.e.m