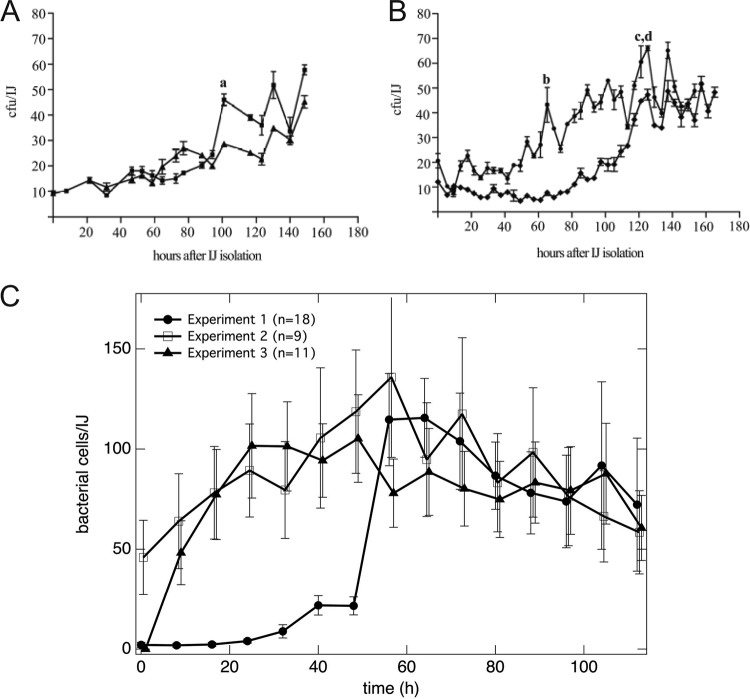
FIG 5 .
Comparison of traditional grinding experiments with microfluidic device experiments for quantification of X. nematophila bacterial population dynamics in S. carpocapsae nematodes. (A and B) Traditional grinding experiments include surface sterilization, grinding a subpopulation of nematodes, plating on synthetic medium, and performing bacterial CFU counts. Subpopulations of immature IJs were isolated and assayed every 4 to 8 h. Panels A and B show two replicates each from two separate experiments; each point is the average result for three individual assays. Error bars indicate standard errors of three measurements of the population at each time. Lowercase letters a to d represent time points that were used to calculate maximum growth rate in previous research (23). (C) Analysis of epifluorescence micrographs of GFP-expressing X. nematophila in individual S. carpocapsae nematodes trapped in a microfluidic device. Each plot represents the average from all living nematodes in the experiment. Error bars indicate standard errors of the population distribution. (Panels A and B are republished from reference 23.)