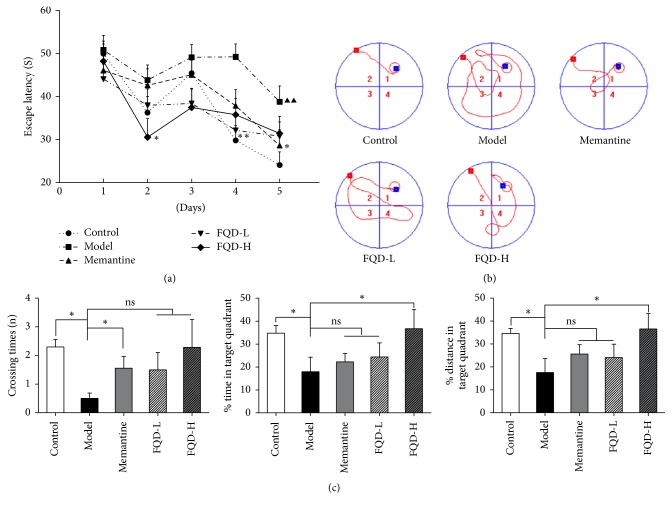
Figure 2.
FQD ameliorated learning and memory deficits of SAMP8 mice. (a) All the group displayed a spatial learning effect (p < 0.01 or p < 0.05). On the last 2 days of training, the model group exhibited longer latencies to reach the platform than the control group (p < 0.01). Moreover, compared to the model group, memantine, FQD-L, and FQD-H groups exhibited shorter latencies to reach the platform on the fifth (p < 0.05), fourth (p < 0.01), and second (p < 0.05) days of training. (b) The strategies for searching platform on the fifth day of navigation trial. (c) Values representing the number of crossings, swim time, and percent distance in the target quadrant were all significantly lower in the model group compared to the control group (p < 0.05). Compared to the model group, the number of crossings exhibited by the memantine group and the swim time and percent distance in target quadrant of the FQD-H group were significantly higher (p < 0.05). No between-group difference was observed in terms of total swim distance throughout the test (p > 0.05). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01 between model and drug-treated groups. Black triangle, p < 0.01 between model and control group.