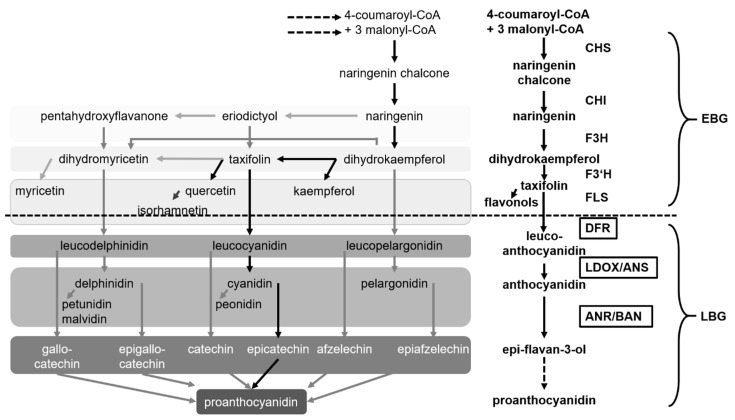
Figure 1.
Flavonoid biosynthesis pathway of plants modified from [22] with an emphasis on A. thaliana seeds. Black arrows highlight the core pathway and substances in A. thaliana discussed in this review. The respective enzymatic steps from the different levels of the pathway are extracted on the right. Examples for different products of OMTs (O-METHYLTRANSFERASEs) are given (isorhamnetin, peonidin, petunidin, malvidin). Note that not all steps occur in A. thaliana and other substances can also occur in A. thaliana: e.g., pelargonidin. See [22] for details. The dashed arrow indicates that several proteins and enzymes are required for proanthocyanidin synthesis, deposition and/or further conversion to condensed tannins including transport processes (for a review on flavonoid transport and a few recent findings, see [24,25]). R2R3-MYELOBLASTOSIS-basic HELIX-LOOP-HELIX-WD40 repeat (MBW(AtTTG1)) complexes predominantly regulate late biosynthetic genes encoding for the core pathway enzymes. Dashed line: the assumed “border” between early and late biosynthetic genes and products in A. thaliana [20,26,27]. Boxed enzymes are under differential developmental regulation of MBW(AtTTG1) complexes. See Section 6 for details. Reduced levels of isorhamnetin in seeds of ttg1-1, but not transparent testa (tt)2 and tt8 mutants, indicate that the border might need some adjustment or that additional AtTTG1-dependent regulation occurs [22]. CHS: CHALCONE SYNTHASE, CHI: CHALCONE ISOMERASE, F3H: FLAVANONE 3-HYDROXYLASE, F3′H: FLAVONOID 3′ HYDROXYLASE, FLS: FLAVONOL SYNTHASE, DFR: DIHYDROFLAVONOL 4-REDUCTASE, LDOX: LEUCOANTHOCYANIDIN DIOXYGENASE, ANS: ANTHOCYANIDIN SYNTHASE, ANR: ANTHOCYANIDIN REDUCTASE, BAN: BANYLUS, EBG: early biosynthetic genes, LBG: late biosynthetic genes.