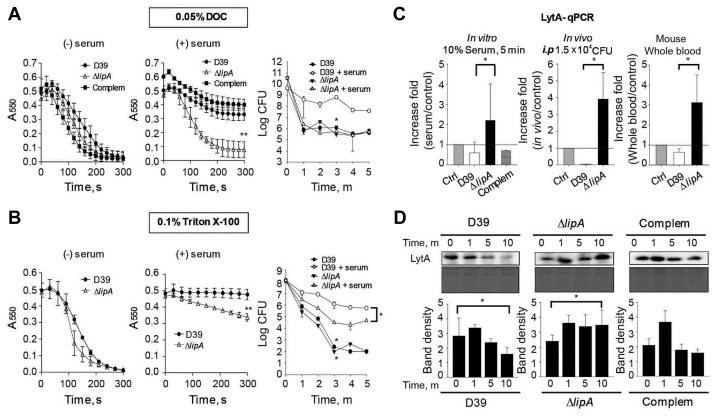
Fig. 5. Inhibition of autolysis and LytA expression by LipA in vitro and in vivo.
Pneumococcal strains cultured in THY broth until log phase were incubated with 10% goat serum for 10 min. (A, B) 0.05% DOC (A) and 0.1% Triton X-100 (B) were added to the bacterial culture and absorbance at 550 nm or viable cell number was determined. (C) (left) Pneumococcal strains cultured in THY broth to the log phase were incubated with 10% goat serum for 5 min, and lytA mRNA was analyzed by qPCR (middle). Mice were infected with 1.5 × 104 CFU of pneumococcal strain intraperitoneally (i.p.). At the severely morbid stage, mouse blood was collected, and lytA RNA expression was analyzed by qPCR (right). The pneumococcal strain at the log phase was incubated with whole mouse blood for 15 min, and lytA mRNA was analyzed by qPCR. Each mouse sample was analyzed in triplicate, and the Mann–Whitney rank sum test was used for statistical analysis (*p ≤ 0.05). Control bar (Ctrl) was displayed one fold value (control/ control). (D) Pneumococcal strains cultured in THY broth to the log phase were incubated with 10% goat serum for 0, 1, 5, and 10 min. The LytA level was determined by western blotting. SDS-PAGE results following Coomasie Blue staining are displayed and served as a loading control. Band density was analyzed by ImageJ. (A, B, C-left, D) Representative data are displayed from three independent experiments and analyzed by one-way ANOVA (*p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01).