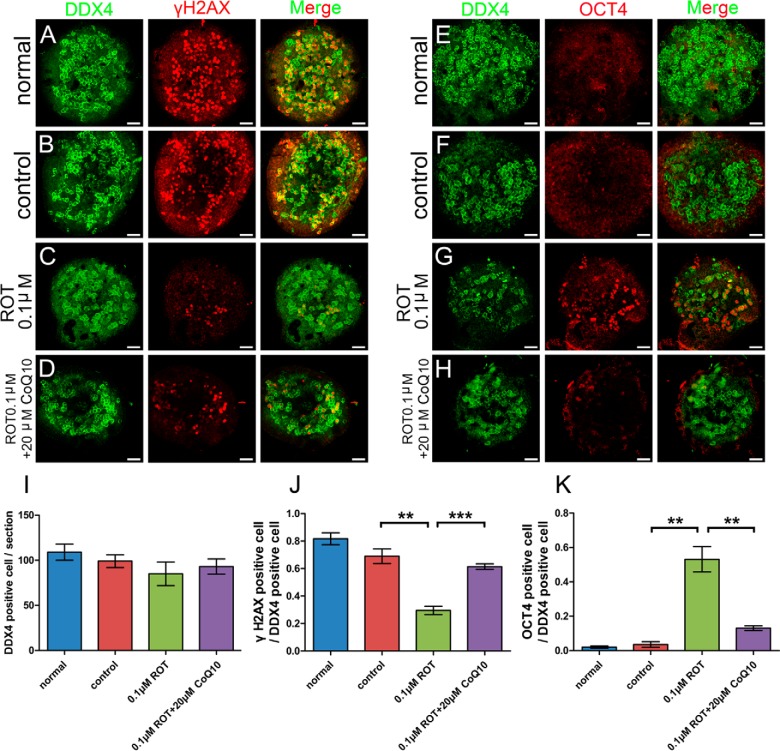
Fig. 5.
Disruption of the electron transport chain inhibits entry of female germ cells into meiosis, and CoQ10 rescues the phenotype. Rotenone (0.1 μm) treated (C, G) organ cultures showed decreases in the number of meiotic cells, based on staining for γH2AX (meiotic cell marker), compared with in the normal (A) and control (DMSO) (B) groups; oogonia were clearly increased, based on staining for OCT4 (oogonia marker), compared with staining in the normal (E) and control (DMSO) (F) group; whereas, total germ cell numbers were not different, based on counts of DDX4 (germ cell marker) positive cells (I). Compared with the normal (A, E) and control (B, F) groups, adding 20 μm CoQ10 (D, H) could rescue the phenotype. Bar graphs (I–K) showed the results of stained cell counting. Error bars indicate S.E. and similar experiments were each repeated at least three times (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, Student's t test). Bar, 50μm.