Fig. 1.
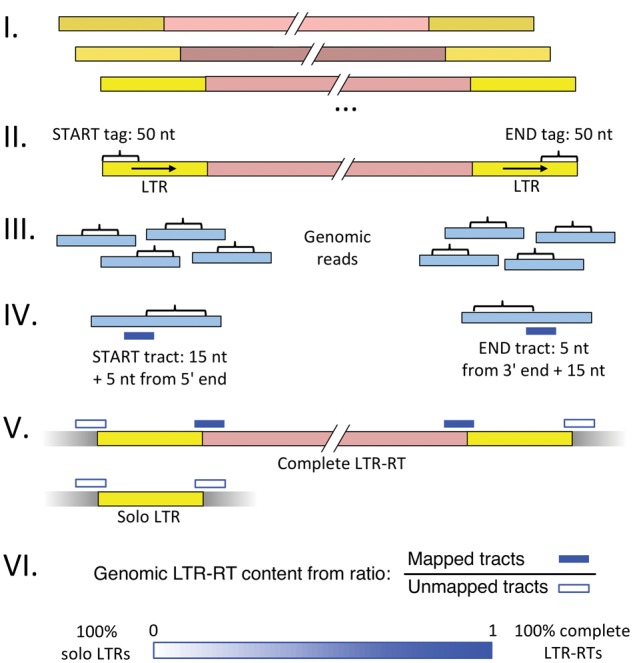
—Method to estimate ratio of solo-long terminal repeats (LTRs) to complete LTR-retrotransposons (RTs) within a species. (I) Retrieve or assemble 3 to 10 paralogs for each LTR-RT group. (II) Extract 50-nt START and END tags from LTRs of paralogs. (III) Find genomic reads matching START and END tags with RepeatMasker (Smit et al. 2015), allowing for mismatches. (IV) For each matching read, extract a 20-nt tract containing 5 nt from the tag and 15 nt flanking sequence. Tracts are taken from the 5′ or 3′ ends of START or END tag matches, respectively. (V) Map each tract to the LTR-RT paralogs collected in (I) using BWA ALN (Li and Durbin 2009), allowing for mismatches. Count the numbers of mapped (M) and unmapped (U) tracts. Genomic reads covering complete LTR-RTs yield tracts that are mapped and unmapped in equal numbers, while genomic reads covering solo LTRs produce only unmapped tracts. (VI) The relative genomic content of solo LTRs to complete LTR-RTs is inferred from the ratio of mapped to unmapped tracts. See “Methods” section for further details and pipeline validation results.
