Table 1.
Essential oils constituents with antinociceptive activity.
| Compound | Experimental Protocol | Antinociceptive Activity and/or Mechanism | Animal Tested and/or Cell Line | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Formalin, capsaicin and glutamate-induced orofacial nociception | Decreased rubbing behavior | Male Swiss mice | [19] |
| Acetic acid-induced writhing, formalin and hot plate tests CG-induced inflammation |
Reduced writhes, and liking time Increased latency time of liking and jumping behavior Reduced leukocyte migration |
Male Swiss mice | [20] | |
| Tail flick test CG, TNF-α, PGE2 and dopamine-induced hypernociception CG-induced pleurisy LPS-induced NO secretion Fos protein immunofluorescence |
Increased latency time response Decreased mechanical hypernociception Reduced leukocyte and neutrophils migration and TNF-α level Reduced NO production Increased c-Fos immunoreaction |
Male Swiss mice Macrophage Periaqueductal grey neurons |
[25] | |
| Acetic acid-induced writhing and formalin tests | Reduced writhes, and liking time | Male Swiss mice | [31] | |
 |
Acetic acid-induced writhing test Formalin test Hot plate test Peritoneal permeability induced by acetic acid |
Reduced the number of abdominal contortions Inhibited nociception in both the first phase and second phase Caused a significant latency prolongation Inhibited the acetic acid-induced peritoneal capillary permeability |
Male albino Swiss mice | [241] |
 |
Acetic acid-induced writhing, formalin and hot plate tests | Reduced writhes, and paw-liking time Increased latency time response |
Male Swiss mice | [40] |
| CG, TNF-α, PGE2 and dopamine-induced hypernociception CG-induced paw edema CG-induced pleurisy LPS-induced nitrite secretion |
Decreased mechanical hypernociception Decreased edema volume Reduced leukocyte migration and TNF-α level Reduced nitrite production |
Male Swiss mice Macrophage |
[42] | |
| Formalin, capsaicin and glutamate-induced orofacial nociception | Reduced face-rubbing behavior |
Male Swiss mice | [43] | |
| Whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings | Increased secretion of l-glutamate Membrane hyperpolarization |
Rat spinal cord | [44] | |
 |
Whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings Intracellular recordings |
Inhibition of excitability Generation of action potentials |
Male and female Wistar rat sciatic nerve and dorsal root ganglia | [47] |
 |
von Frey test (electronic version) | Reduced mechanical allodynia | Male ddY-strain mice (sciatic nerve ligation) | [56] |
| Formalin test | Reduced licking and biting behavior | Male ddY-strain mice | [62] | |
| Xylene-induced ear edema and formalin-induced hind paw edema COX-2 expression and inflammatory infiltrates immunohistochemistry |
Reduced edema volume Decreased COX-2 expression and inflammatory infiltrates |
Male Kunming mice | [64] | |
| Formalin and hot plate tests c-Fos immunohistochemistry |
Increased latency time of hindpaw withdrawl Increased c-Fos expression in hypothalamic orexin neurons |
Wild type mice (C57BL/6) Orexin neuron-ablated mice Orexin peptide-deficient mice |
[65] | |
 |
Paclitaxel-induced acute pain (von Frey filaments) | Inhibiton of mechanical allodynia and hypernociception | Male ddY-strain mice | [48] |
 |
Formalin, capsaicin and glutamate-induced orofacial nociception Field potential recordings |
Reduced face-rubbing behavior Inhibition of field potentials |
Male Swiss mice Hippocampal dentate gyrus |
[53] |
| Acetic acid-induced writhing, formalin and hot plate tests CG-induced peritonitis |
Reduced writhes, and paw-liking time Increased latency time response Inhibition of leukocyte migration and TNF-α level |
Male Swiss mice | [67] | |
| Chronic noninflammatory muscle pain model c-Fos protein immunofluorescence |
Inhibition of mechanical hypernociception Neuron activation |
Male Swiss mice | [69] | |
 |
Acetic acid-induced writhing and formalin tests Substance P and glutamate-induced nociceptive behavior |
Reduced writhes, and paw-liking/biting behavior Reduced nociceptive response |
Male ICR mice | [73] |
| Lingual irritation method | Oral irritation desensitization Increased innocuous warmth and noxious heat sensation |
Human subjects | [83] | |
| Acetic acid-induced writhing test and glutamate-induced nociception Glutamate, AMPA, kainate, substance P and TNF-α-induced pain |
Reduced writhes Reduced nociception Inhibition of biting behavior |
Male Swiss mice | [71] | |
| Monoiodoacatate-induced osteoarthritis von Frey filaments method Spinal pain-related peptide analysis |
Altered gait parameters Reduced mechanical allodynia Reduced expression of substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide Increased dynorphin level |
Sprague Dawley rats Spinal cord samples |
[80] | |
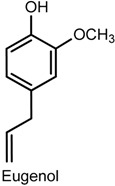 |
Sciatic nerve constriction von Frey and hot plate tests Biochemical assay |
Inhibition of mechanical hypernociception Increased latency time response Reduced IL-1β level |
Male C57BL/6J mice Sciatic nerve |
[79] |
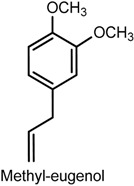 |
Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings | Inhibition of peripheral nerve Nav1.7 currents | Chinese hamster ovary cells | [86] |
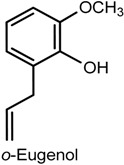 |
Acetic acid-induced writhing, glutamate and hot plate tests Acetic acid-induced peritoneal permeability CG-induced peritonitis |
Reduced writhes and licking time Increased latency time response Inhibition of vascular permeability Reduced TNF-α and IL-1β levels |
Male Swiss mice | [87] |
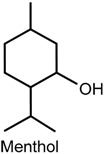 |
Complete Freund’s adjuvant-induced mechanical and thermal hypersensitivity Formalin-induced nociception Electrophysiological recording |
Reduced mechanical and thermal allodynia Reduced paw-licking and lifting behavior Blockage of voltage-gated sodium and calcium channels Reduced neural excitability Blockage of spontaneous synaptic transmission |
D1-male mice Mouse pup spinal cord dorsal horn neurons |
[94] |
| Quantitative sensory testing | Provoked cold hypersensitivity | Human subjects | [46] | |
 |
Acetic acid-induced writhing, hot plate, tail flick, and Complete Freund’s adjuvant tests Capsaicin-induced pain |
Reduced writhes and licking, fliching and biting behavior | C57BL/6 wild-type mice Trp1-/- and Trpm8-/- mice |
[88] |
| Calcium ion-imaging Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings Sensory irritation tests |
Inhibition of TRPV1 currents Reduced skin irritation |
Human embryonic kidney 293 cells Human subjects |
[101] | |
 |
Acetic acid-induced writhing and formalin tests CG and dextran-induced paw edema CG-induced peritonitis and Neutrophil myeloperoxidade (MPO) assay |
Reduced writhes and paw-licking time Inhibition of edema formation Inhibition of MPO activity Reduced neutrophil migration and TNF-α migration |
Male Swiss mice Rat |
[107] |
| Cyclophosphamide and mustard oil-induced visceral nociception Croton oil, arachidonic acid and phenol-induced ear edema |
Inhibition of nociceptive behavior Inhibition of ear edema formation |
Male Swiss mice | [114] | |
| Acetic acid, formalin, capsaicin and mustard oil-induced visceral nocicpetion | Reduced writhes Inhibition of nociceptive behavior |
Male Swiss mice | [115] | |
| Electrophysiological recordings Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings |
Inhibition of α7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptors Inhibition of choline-induced currents |
Frog oocytes (Xenopus laevis) Male Sprague Dawley rat hippocampus |
[116] | |
 |
Formalin test Capsaicin and glutamate-induced orofacial nociception CG-induced pleurisy |
Reduced face-rubbing behavior Inhibition of nociceptive response Reduced TNF-α level |
Male Swiss mice | [119] |
 |
Quantitative sensory testing | Provoked heat hypersensitivity | Human subjects | [46] |
| Acetic acid induced writhing Eddy’s hot plate methods |
Reduced nociception Exhibited hyperalgesic behavior |
Swiss albino mice | [125] | |
 |
Formalin test, capsaicin test and glutamate-induced nociception | Reduced the pain-related behaviors and decreased face-rubbing behavior | Male Swiss mice | [131] |
 |
Mechanical nociception induced by CG, TNF-α, PGE2 and DA | Reduced mechanical nociception induced by TNF-α, PGE2, DA and carrageenan | Male Swiss mice | [130] |
 |
Acetic acid-induced abdominal constrictions, formalin-induced nociception, hot plate test and carrageenan-induced pleurisy | Reduced nociception, inhibited neutrophil infiltration and decreased levels of TNF-α in the exudates | Male Swiss mice | [139] |
| Formaline and capsaicin tests, and glutamate-induced nociception | Decreased orofacial nociceptive behavior | Male Swiss mice | [140] | |
| Mechanical hyperalgesia induced by CG, TNF-α, PGE2 and DA | Attenuated mechanical hyperalgesia induced by CG, TNF-α, PGE2 and DA | Male Swiss mice | [141] | |
 |
Acetic acid-induced writhing test and paw licking induced by formalin, glutamate, capsaicin, menthol, cinnamaldehyde, acidified saline, PMA and 8-Br-cAMP | Reduced the acute pain induced by acetic acid, formalin, glutamate, capsaicin, menthol, PMA and 8-Br-cAMP | Male Swiss mice | [142] |
 |
Acetic acid-induced abdominal writhing, formalin, capsaicin and glutamate tests Mechanical hypernociception and carrageenan-induced inflammatory hypernociception |
Decreased the nociceptive response Reduced the hypernociception index |
Male Swiss mice | [156] |
 |
Acetic acid writhing reflex, hot plate test, and formalin-, capsaicin- and glutamate-induced nociception | Showed central analgesic properties and reduced nociceptive response induced by acetic acid, formalin, glutamate and capsaicin | Male Swiss mice | [160] |
 |
Eddy’s hot plate method | Increased the latency period, suggesting a potential central analgesic activity | Adult Wistar rats | [166] |
| Carrageenan induced paw edema | Decreased the paw volume | Adult Wistar rats | [167] | |
| Tail flick method and carrageenan induced rat paw edema | Showed antinociceptive effect and decreased the paw volume | Adult Wistar rats | [168] | |
 |
Acetic acid-induced abdominal writhings, formalin-induced nociception, hot plate test, grip strength test and carrageenan-induced peritonitis | Reduced the antinociceptive behavior, increased the latency time and decreased the leukocyte migration to the peritoneal cavity | Male Swiss mice | [175] |
 |
Segmental spinal nerve ligation-induced neuropathic pain and complete Freund’s adjuvant-induced inflammatory pain | Attenuated mechanical hyperalgesia through activation spinal GABAergic transmission in the spinal cord | Male adult ICR mice | [176] |
 |
Acetic acid-induced writhing Paw licking induced by formalin, glutamate and capsaicin Hot-plate test Paw edema induced by compound 48/80, serotonin, histamine or PGE2 Carrageenan-induced peritonitis |
Inhibited acetic acid-induced nociception Decreased time of licking the paw Did not change the latency reaction time Reduced the paw edema and Reduced the cytokine levels |
Male Swiss mice | [183] |
 |
Formalin test and hot plate test | Inhibited both phases of the formalin test and augmented the latency reaction time in hot plate | Male Swiss mice | [3] |
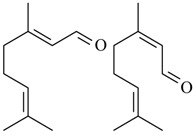 (geranial) (neral) Citral (= geranial + neral) |
Acetic acid-induced writhing and formalin induced nociception | Inhibited the abdominal constrictions induced by acetic acid and reduced nociceptive behavior | Male Swiss mice and male Wistar rats | [131] |
| Formalin-induced nociception, Mechanical hyperalgesia Pain behaviour induced by glutamate, capsaicin, and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate |
Inhibited formalin-induced licking Reduced mechanical hyperalgesia Inhibited the nociceptive response |
Male Swiss mice | [189] | |
 |
Whole-cell patch-clamp recording | Increased the frequency of spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic current | Adult Wistar rat | [194] |
 |
Heterologous expression in HEK293 cells H2O2-induced nociception |
Stimulated primary sensory neurons Reduced nociceptive behaviors via H2O2-induced TRPA1 activation |
Adult Swiss mice | [199] |
 |
Oxazolone-induced colitis model Nociceptive behavior assay |
Alleviated pathological alterations induced by oxazolone Reduced the levels of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-13 and TNF-α) |
Male BALB/c mice | [203] |
 |
Paw edema induced by carrageenan and Complete Freund’s adjuvant Mechanical hypernociception induced by prostaglandin, carrageenan and Complete Freund’s adjuvant |
Reduced the paw edema and level of some cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-17) Decreased hypernociceptive response induced by carrageenan but was not able to alter the PGE2-induced mechanical hypernociception |
Male Swiss mice | [212] |
 |
Acetic acid-induced writhing Formalin test Complete Freund adjuvant-induced pain (CFA) Hot-plate test Glutamate test |
Reduced the total number of writhing Decreased paw licking times during the second phase of the formalin test Decreased peripheral nociception induced by CFA Did not alter the latency time in the hot plate test Reduced paw edema in the glutamate test |
Male Swiss mice | [213] |
 |
Dorsal root ganglia (DRG) neurons and TRPV1-expressing HEK293 cells | Did not provoke any membrane damage and promoted an elevation of the cytosolic calcium levels in DRG neurons | Old Wistar rat | [222] |
 |
Acetic acid-induced writhing test ormalin test Hot plate test Carrageenan-induced paw edema Carrageenan-induced peritonitis |
Decreased the total number of writhing Reduced the licking time in both phases Did not increase latency in the hot-plate test Decreased carrageenan-induced paw edema Inhibited the production or action of some proinflammatory cytokines |
Male Swiss mice | [217] |
 |
Acetic acid-induced writhing test Formalin-induced nociception |
Reduced the number of abdominal contortions Inhibited both phases of the pain stimulus |
Male albino Swiss mice | [226] |
 |
Capsaicin test | Attenuated the capsaicin-induced nociceptive response and this effect was mediated by peripheral CB2 receptor activation | Male Swiss mice | [234] |
CG: carrageenan; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor α; PGE2: prostaglandin E type 2; LPS: lipopolysaccharide; NO: nitric oxide; COX-2: ciclo oxigenase type 2; ICR: Institute of Cancer Research; AMPA: adenosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate; IL: interleucin; TRPV: transient receptor potential vanilloid; DA: dopamine; PMA: phorbol myristate acetate; 8-Br-cAMP: 8-bromo-adenosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate; GABAergic: γ-aminobutyric acid; TRPA: transient receptor potential ankyrin; CB2: cannabinoid receptor type 2.
