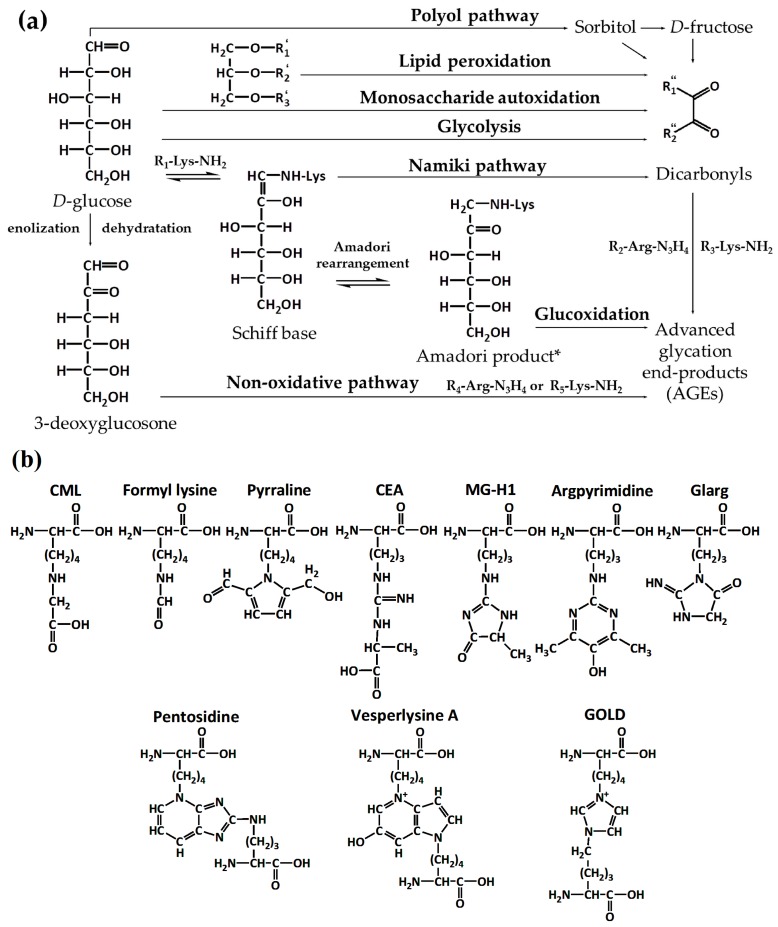
Figure 1.
Pathways of early and advanced glycation (oxidative glycosylation [12], Namiki pathway [13], enolization [14], oxidative [15] and non-oxidative (enolization and dehydration stages are not mentioned) [16] degradation of early glycation products, polyol pathway [17] and lipid peroxidation [18] (a) and structures of major AGEs detected in vivo and in thermally processed foods (b)). R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, polypeptide chains; R1′, R2′, R3′, fatty acid residues; R1′′ = H, R2′′ = H for glyoxal; R1′′ = H, R2′′ = CH3 for methylglyoxal; R1′′ = H, R2′′ = C4H9O3 for 3-DG. * Ketoses form so-called Heyns products.