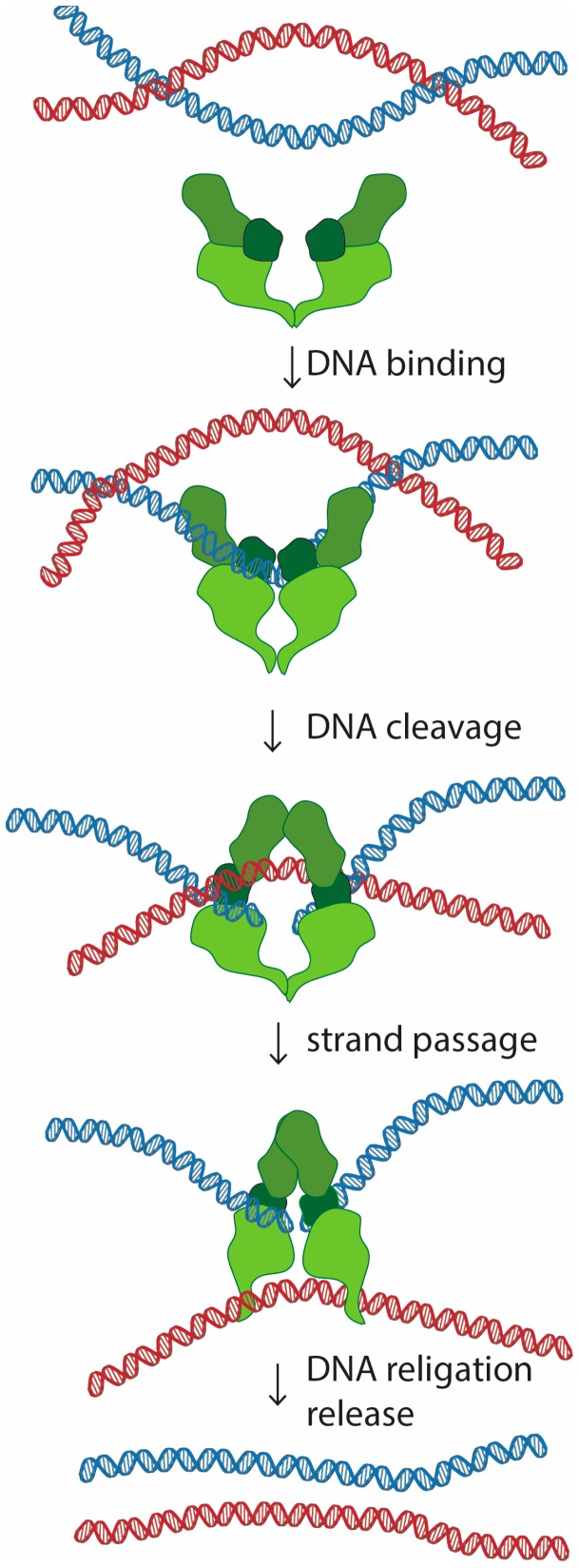
Figure 1.
Mechanism of DNA decatenation by topoisomerase II. Topoisomerase II binds to one of the entangled (catenated) DNA molecules. The reaction involves cleavage of the bound DNA strand (blue), introducing a double strand break. Topoisomerase II remains covalently connected to the cut DNA, preventing its dissociation. Once the continuity of one of the DNA strands is severed, topoisomerase II can transport the other DNA molecule (marked in red) through the created gap. Upon strand passage, the cleaved DNA is ligated back together, and topoisomerase II releases the DNA molecule.