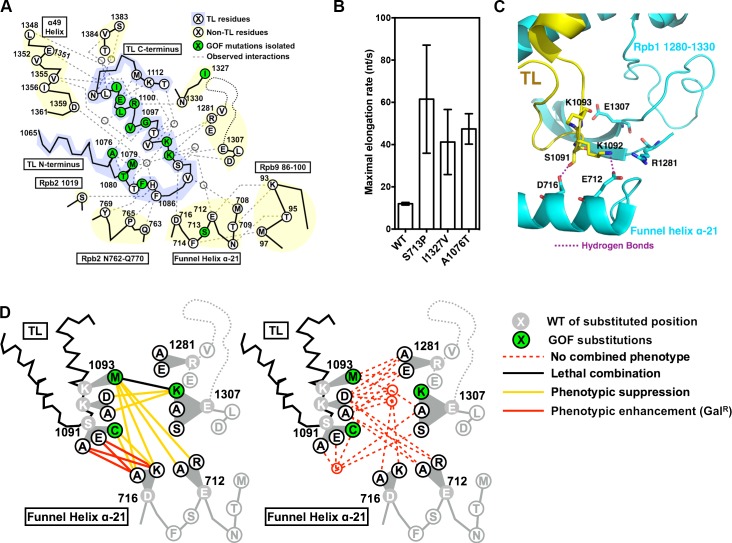
Fig 5. Functional contribution of TL tip and funnel helix α-21 to proper TL dynamics.
(A) Observed and predicted interactions between TL and TL-proximal domains. TL schematic is shown with residues identified by single-letter amino acid code and positions of interest annotated. Positions of GOF mutants isolated in our screen, along with the positions for a subset of previously isolated TL-proximal GOF mutants, are color coded in green. Observed TL interactions with other Rpb1 domains from structures or simulation studies are shown as grey dashed lines. (B) Maximal in vitro elongation rates (nucleotides/second) of Pol II WT and genetic GOF mutants S713P, I1327V and A1076T. (C) Observed interactions between open TL tip and TL adjacent charged residues (PDB: 5C4X). Funnel Helix refers to the Rpb1 α-21 alpha-helix. (D) Genetic interactions between the TL tip and proximal Rpb1 domains. Schematics of the TL and adjacent domains are shown in lines, with positions of interest shown in single-letter amino acid code. Substituted residues are shown in grey, with substituting amino acids shown in white or green filled circles based on single substitution phenotypes (S8F Fig). Double substitution phenotypes are shown as colored lines connecting the two relevant single substitutions. Some sets of similar interactions were grouped into nodes to reduce complexity in interaction lines.