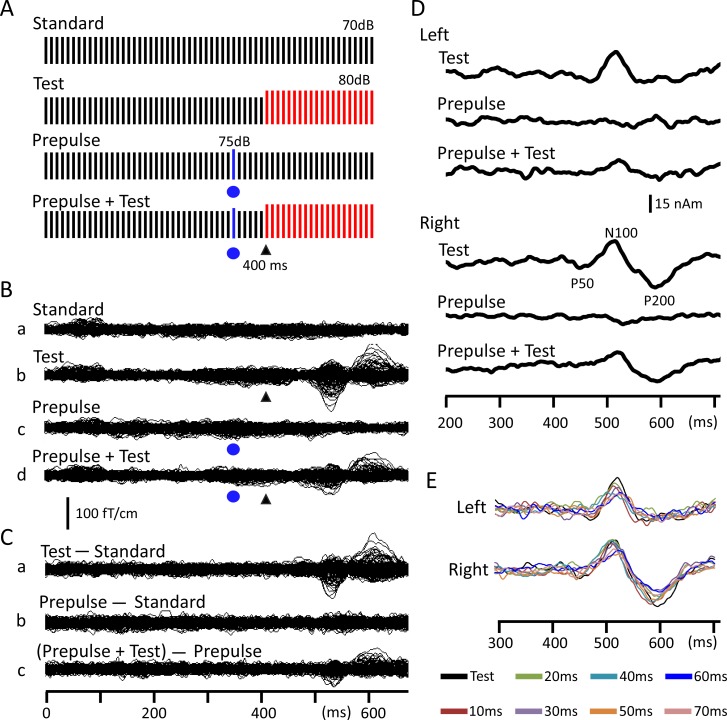
Fig 1. Change-related cortical response and its inhibition by a weak prepulse.
(A) Sound stimuli consisted of a train of 1-ms clicks at 100 Hz in repetitive frequency and 70 dB SPL in sound pressure. An abrupt increase of 10 dB in sound pressure was used to evoke the Test response, while that for the prepulse (5 dB) was used to inhibit the Test response. Each bar indicates a single click. (B) An example of prepulse inhibition of the change-related auditory response by a prepulse presented 60 ms before the Test stimulus in a representative subject. Recorded MEG waveforms in the Pre run of the Placebo session for the Standard (Ba), Test (Bb), Prepulse (Bc), and Prepulse + Test (Bd) stimuli are shown. The Test alone MEG response (Ca) was obtained by subtracting the waveform for the Standard stimulus (Ba) from that for the Test stimulus (Bb). The Prepulse alone response (Cb) was obtained by subtracting the waveform for the Prepulse stimulus (Bc) from that for the Standard (Ba). The Prepulse + Test response (Cc) was obtained by subtracting the waveform for the Prepulse stimulus (Bc) from that for the Test + Prepulse stimulus (Bd). (D) Time course of the source strength of dipoles obtained from MEG waveforms in C. (E) The source strength waveforms for all eight PTI conditions in this run. Filled blue circles and black arrow heads indicate the presentation of the prepulse and test stimulus, respectively.