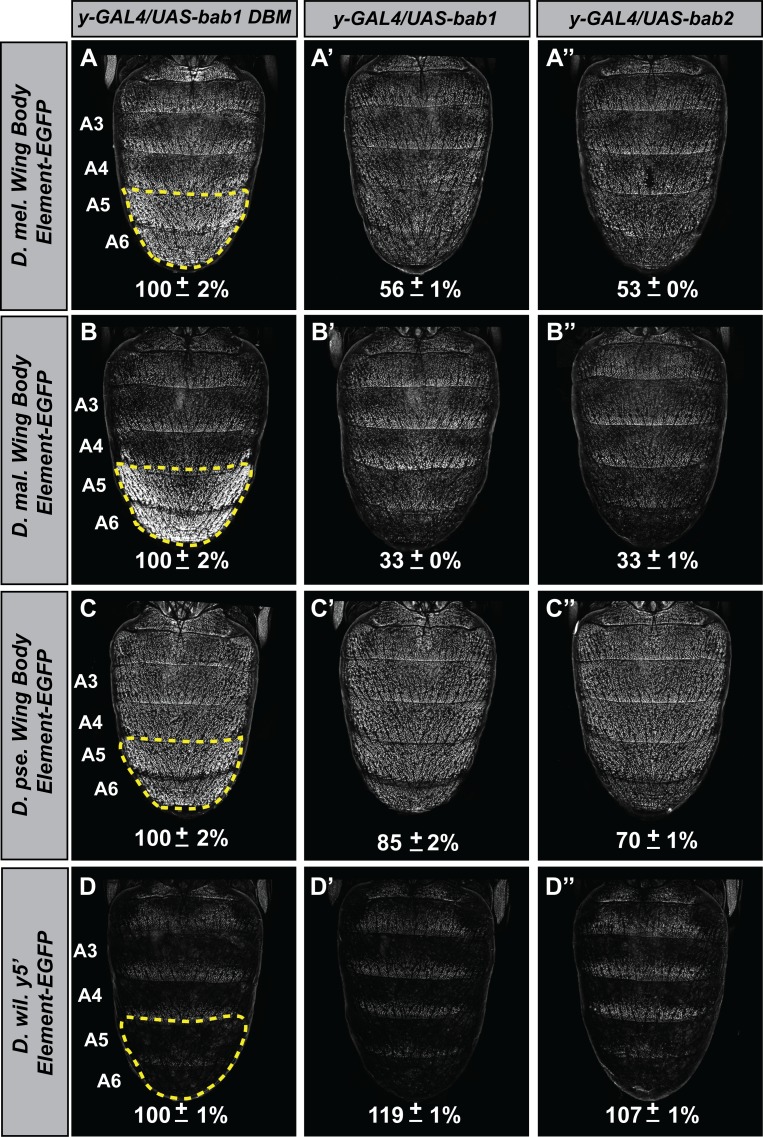
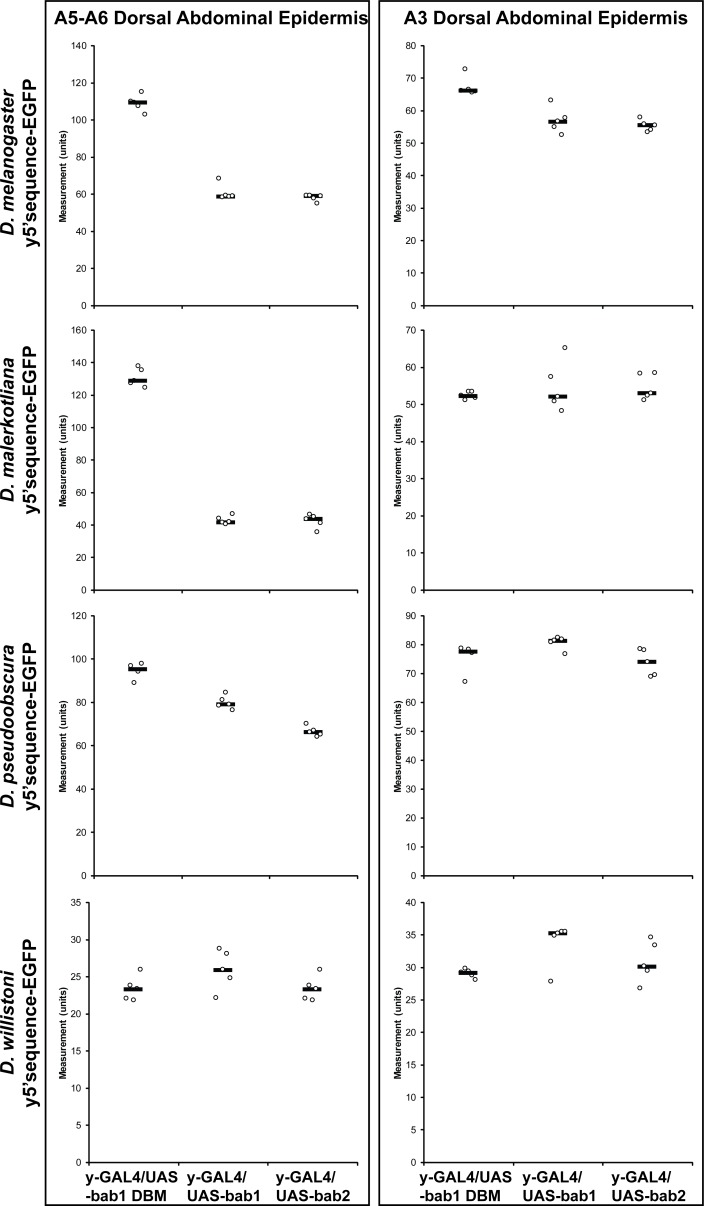
Figure 8. The evolved repression by Bab for cis-regulatory regions 5’ of yellow.
(A–A’’) Comparison of the levels of EGFP-reporter expression in the male A5 and A6 segments driven by the Wing Body Element of D. melanogaster. (B–B’’) Comparison of the levels of EGFP-reporter expression in the male A5 and A6 segments driven by the Wing Body Element of D. malerkotliana. (C–C’’) Comparison of the levels of EGFP-reporter expression in the male A5 and A6 segments driven by the Wing Body Element of D. pseudoobscura. (D–D’’) Comparison of the levels of EGFP-reporter expression in the male A5 and A6 segments driven by the 5’ non-coding region of D. willistoni yellow. For each comparison, the level of EGFP expression are expressed as the percentage of the mean ±SEM for samples in which the Bab1-DBM was expressed. (A–D) Ectopic expression of the Bab1-DBM in the y-GAL4 pattern. (A’–D’) Ectopic expression of Bab1 in the y-GAL4 pattern. (A’’–D’’) Ectopic expression of Bab2 in the y-GAL4 pattern.