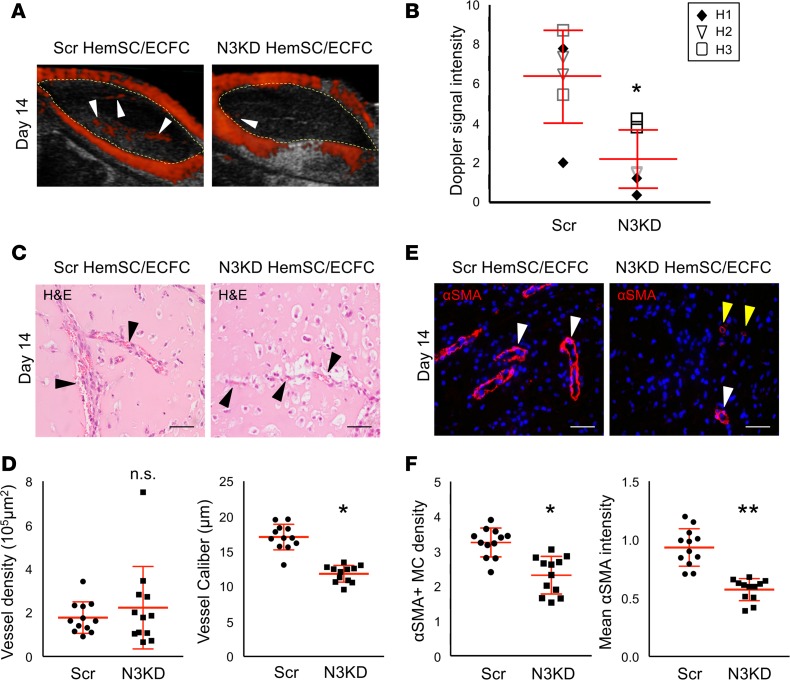
Figure 5. NOTCH3 activity is required for HemSC mural cell differentiation and IH development in a mouse model of IH.
NOTCH3-knockdown (N3KD) HemSCs or Scr HemSCs in a 1:1 ratio with ECFCs were resuspended in Matrigel, and subcutaneously implanted into the flanks of immunocompromised mice. (A) Detection of high blood flow by ultrasound Doppler in Scr HemSC/ECFC and N3KD HemSC/ECFC xenografts at day 14 after implantation. Xenograft area marked with yellow dotted line. White arrowheads mark Dopplerable blood flow (red). (B) Scatter plot of mean Doppler signal intensity normalized by xenograft area (n = 3 populations: H1, H2, H3; n = 2 implants each). Average mean intensity denoted with a horizontal line. Error bars represent ± SD. *P < 0.03, 1-way ANOVA. (C) H&E staining of Scr HemSC/ECFC and N3KD HemSC/ECFC xenograft sections. Arrowheads mark red blood cell–containing vessels. (D) Quantification of vessel density and caliber (n = 3 populations; n = 2 implants each). Error bars represent ± SD. *P < 0.0002, 1-way ANOVA. (E) Scr HemSC/ECFC and N3KD HemSC/ECFC xenograft sections stained for αSMA. White arrowheads mark vessel surrounded by αSMA+ mural cells. Yellow arrowheads mark vessel surrounded by mural cells that express low levels of αSMA. (F) αSMA+ mural cell density determined as mean mural cell αSMA signal intensity normalized to IH endothelial GLUT1 signal intensity. Average mural cell αSMA expression determined as mean αSMA signal intensity–normalized DAPI+αSMA+ cell number (n = 3 populations; n = 2 implants each). Error bars represent ± SD. n.s., not significant. *P < 0.0002, **P < 0.000005, 1-way ANOVA. Scale bars: 50 μm. αSMA, α smooth muscle actin; ECFC, endothelial colony-forming cell; GLUT1, glucose transporter 1; HemSC, hemangioma stem cell; IH, infantile hemangioma, MC, mural cell; Scr, scrambled.