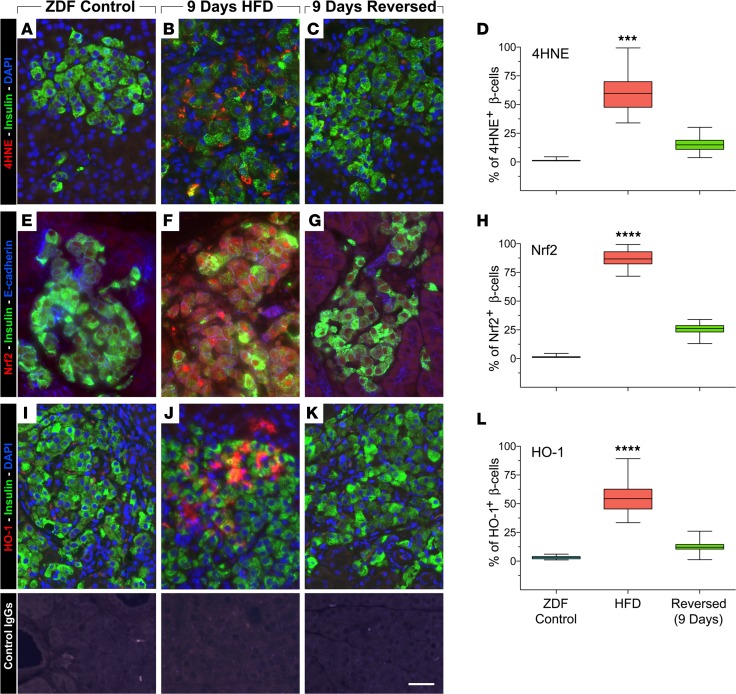
Figure 5. Markers of oxidative stress.
(A) Pancreatic sections were double labeled for insulin (green fluorescence) and 4-HNE (red fluorescence). ZDF rats after 9 days of high-fat diet showed intense cytoplasmic staining for 4-HNE in β cells (B). This was reduced 2 weeks after a return to regular diets (C). Percentage of 4-HNE+ β cells in each animal group (D). Immunostaining for Nrf2 (red fluorescence) revealed substantial immunoreactivity both in the cytoplasm and the nucleus of β cells in ZDF rats fed high fat diets for 9 days (F), when compared with ZDF controls (E). In contrast, 2 weeks after return to regular diets, the immunoreactivity for Nrf2 was dramatically reduced (G). Percentage of 4-Nrf2+ β cells in each animal group (H). Similarly, pancreatic sections stained for HO-1 (red fluorescence) showed increased cytoplasmic and nuclear localization of HO-1 in β cells (green fluorescence), which — after 9 days of HFD — was greatly diminished 2 weeks after return to regular diet (K). Percentage of HO-1+ β cells in each animal group (L). Specificity of detected immunoreactivities was validated by incubation of tissue sections with control IgGs from each species (lower panels). Scale bar: 25 μm. (D, H, and L) One-way ANOVA, ***P < 0.005, ****P < 0.0001.