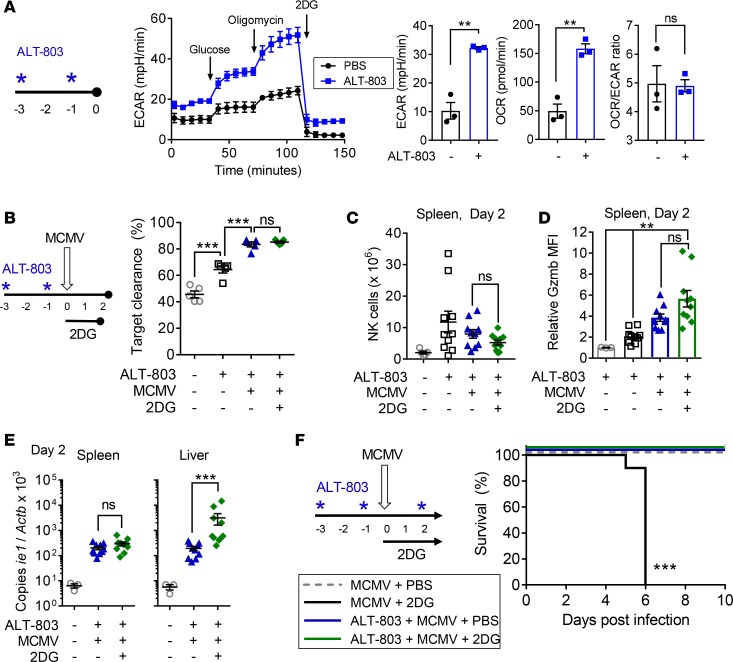
Figure 5. NK activation with ALT-803 rescues MCMV susceptibility caused by 2DG treatment.
(A) Female WT C57BL/6 mice were treated with 5 μg ALT-803 twice, NK cells were purified from their spleens, and a glycolytic stress test was performed. Representative graph showing baseline, normal (+glucose), and maximal (+oligomycin) extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) in control vs. ALT-803–treated mice. Average ECAR, oxygen consumption rate (OCR), and OCR/ECAR ratio are shown after glucose addition (n = 3 individuals/group, 2 separate experiments, 2-tailed t test). (B–E) ALT-803–treated mice were infected with 1 × 105 PFU murine cytomegalovirus (MCMV) and treated with 2-deoxy-ᴅ-glucose (2DG) daily. (B) Clearance of m157-transgenic targets from the spleens of infected and uninfected mice ± ALT-803 and 2DG on day 2 after infection (n = 5/group, representative of 2 experiments, 1-way ANOVA). (C) The number and percentage of NK cells isolated from the spleens or livers of mice in B. (D) Mean fluorescence intensity of granzyme B (Gzmb MFI) in all NK cells from B. (E) Viral copy number measured by quantitative PCR from the spleens and livers collected in B, shown as copies of MCMV ie1 gene/copies of β-actin × 1,000. For C–E, n = 10/group, 2 experiments, 1-way ANOVA, using log-transformed data for E. (F) Mice were given an additional dose of ALT-803 2 days after infection and followed for 10 days. Survival of mice with no treatment (gray dashed line), 2DG treatment (black), ALT-803 treatment (blue), or ALT-803 with 2DG (green) (n = 10/group, 2 experiments, log-rank Mantel-Cox test). Data shown as mean ± SEM or survival. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Asterisks in A, B, and F indicate treatment with ALT-803.