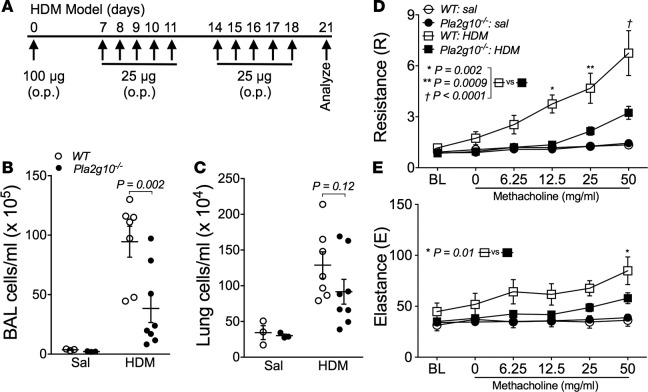
Figure 2. Pla2g10–/– mice are protected from developing airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) and aberrant lung inflammation.
(A) HDM sensitization and challenge model used to induce allergic airway disease. Animals were instilled with 100 μg HDM (protein) on day 0, and then 25 μg HDM (protein) on days 7–11 and 14–18. On day 21, airway mechanics were assessed and mice were sacrificed. o.p., oropharyngeal administration. (B) Cells in the BALF following HDM sensitization and challenge were isolated and counted using an automated cell counter (n = 3/group for Sal, 7 for WT HDM, and 8 for Pla2g10–/– HDM). Mean ± SEM. (C) Single cell suspensions of lung leukocytes following HDM sensitization and challenge were isolated from digested lung tissue and counted using an automated cell counter (n = 3/group for Sal, 7 for WT HDM, and 8 for Pla2g10–/– HDM). Mean ± SEM. (D and E) Measurement of AHR to increasing doses of methacholine following HDM sensitization and challenge using the forced oscillation technique to measure lung mechanics (n = 3/group for Sal, 10 for WT HDM, and 12 for Pla2g10–/– HDM). Mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was determined by 2-way ANOVA with uncorrected Fisher’s LSD.