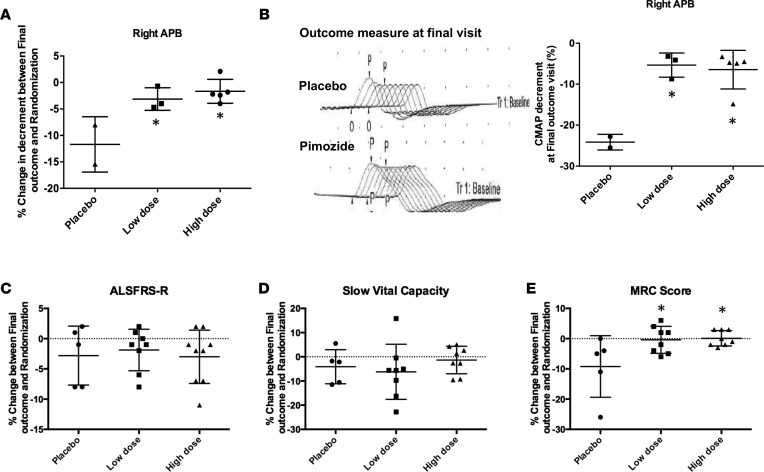
Figure 11. Pimozide improves CMAP decrement in right APB and MRC sum score in ALS patients.
Compound motor action potential (CMAP) recordings of right APB (A) were examined for changes in percent decremental response to repetitive nerve stimulation (RNS) between the randomization visit and end-of-treatment visit. Pimozide significantly improved the percentage change in decremental response in CAMP recordings of right APB. Placebo, n = 2; low dose, n = 3; high dose, n = 5. (B) Examples of CAMP recordings measured at the right APB at the end of placebo or pimozide treatment visits (left panel). Pimozide treatment was found to improve CAMP decrement recorded at the right APB (right panel). (C–E) Revised ALS Functional Rating Score (ALSFRS-R), slow vital capacity (SVC), and MRC sum score were assessed in patients treated with placebo, low dose (2 mg/day), or high dose (4 mg/day or more) of pimozide. The bar graphs represent the change in ALSFRS-R (C), SVC (D), and MRC sum score (E) between randomization and end of treatment visits. *P < 0.05. Placebo, n = 5; low dose, n = 8; high dose, n = 8. Primary outcome measure analyses were performed using nonparametric analyses including Wilcoxon rank-sum test for change scores between end-of-treatment and randomization visits and Kruskal-Wallis H test for comparison between multiple groups with correction for repeated measures. Additional linear mixed model regression analysis was performed for analysis of decremental response change from end of treatment based upon actual dose of pimozide.