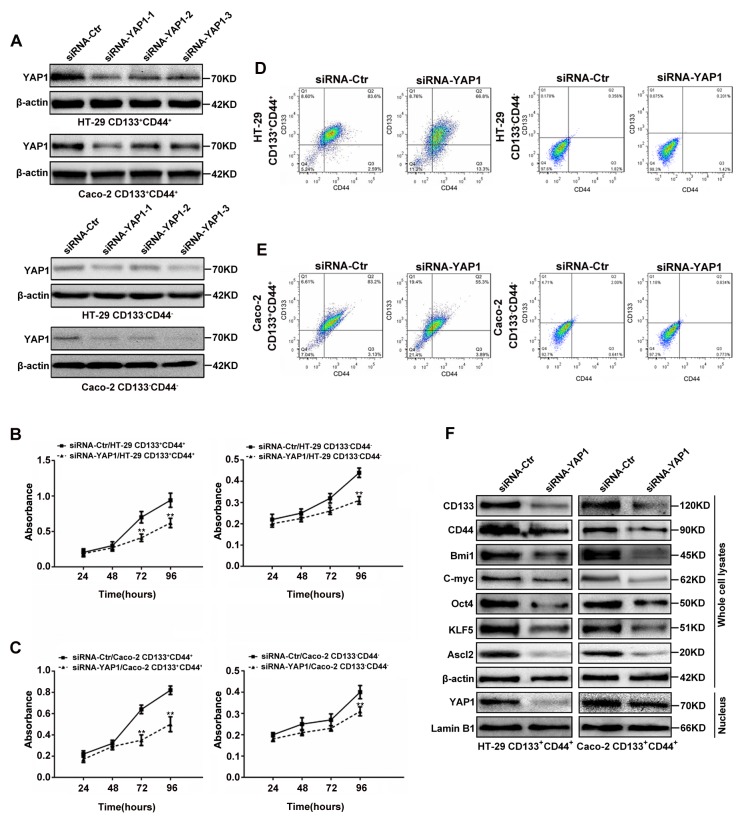
Figure 3. YAP1 knockdown in CD133+CD44+ or CD133-CD44- CRC cells affected their proliferation, CD133+CD44+ percentages, relative gene expression.
(A) Western blots of YAP1 in CD133+CD44+ or CD133-CD44- CRC cells transiently transfected with YAP1 siRNA1 (siRNA-YAP1-1), siRNA2 (siRNA-YAP1-2) or siRNA3 (siRNA-YAP1-3); β-actin was used as a loading control. (B and C) The proliferation rates of CD133+CD44+ and CD133-CD44- HT-29 (B) or Caco-2 (C) cells transfected with siRNA-YAP1-1 from days 1 through 4 after seeding (**: P<0.01). (D and E) The CD133+CD44+ percentages determined by flow cytometry in YAP1-interfered CD133+CD44+ or CD133-CD44- CRC cells. (F) The protein expression levels of Ascl2, KLF5 and ‘stemness’-associated genes in the whole cell lysates of CD133+CD44+ CRC cells transfected with siRNA-YAP1-1; β-actin was used as a loading control. YAP1 nuclear accumulation was inhibited in siRNA-YAP1-1-transfected CD133+CD44+ CRC cells; Lamin B1 was used as an internal control for the nuclear fraction.