Figure 1. Characterization of recombinant oncolytic Vesicular stomatitis viruses expressing human or canine IFNβ and NIS.
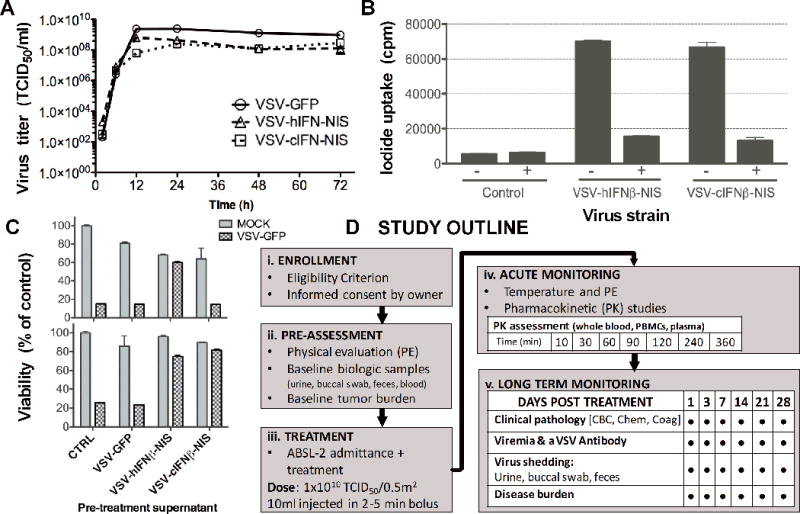
VSV expressing canine or human IFNβ and the sodium iodide symporter (NIS) were tested in vitro to evaluate (A) virus replication in BHK-21 cells by infection with VSV-hIFNβ-NIS, VSV-cIFNβ-NIS or VSV-GFP at a MOI of 3.0 and measurement of virus titer in TCID50; (B) functional NIS expression by measurement of radio-iodide (125I) uptake 24h post infection of BHK-21 cells (MOI 1.0) in the presence (+) or absence (−) of NIS specific inhibitor KCLO4; Expression of (C) functional human or canine IFNβ expression by protection of human Mel-624 or canine MDCK cells respectively following exposure to ultracentrifuged virus infection supernatant (using VSV-GFP cell supernatant as a control), followed by infection with VSV-GFP (MOI 0.1). Cell viability was assessed 48h later by MTT assay and shown as a percentage of control mock infected cells; (D) Veterinary clinical study flow diagram outlining procedures for (i) enrollment, (ii) pre-assessment, (iii) treatment, (iv) acute monitoring, and (v) long-term monitoring.
