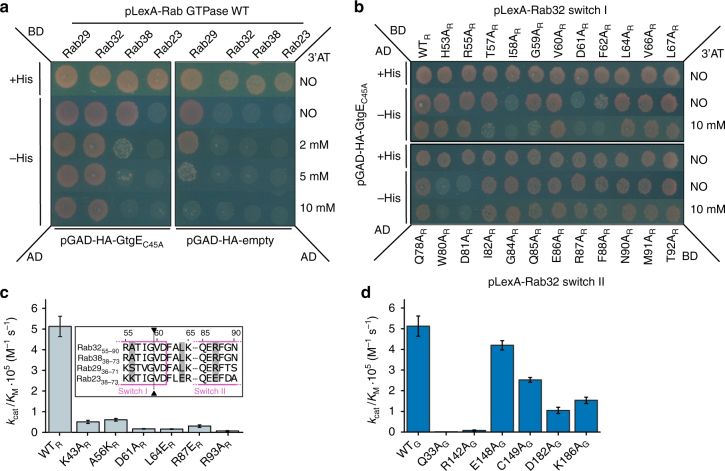
Fig. 4.
Analysis of the Rab32:GtgE complex interface and catalytic mechanism. a Y2H-assay with His growth selection for GtgEC45A (pGAD-HA; prey) binding to full-length Rab29, 32, 38 or Rab23 (pLexA; bait). For probing interaction strength, the growth inhibitor 3-Aminotriazol (3′-AT) was titrated from 0–10 mM. b Mutational alanine screening of the Rab32 switch I (top) and switch II region (bottom) with the Y2H assay. The switch I residues at the GtgE cleavage site display a significant growth defect upon addition of 3′-AT, supporting the Rab32:GDP:GtgEC45A interface. Also, the switch II residues W80R and D81R show decreased complex formation. c Cleavage efficiency of structure and sequence guided Rab32-mutants (8 µM) by GtgE (8 nM) obtained from a densitometric analysis SDS-PAGE-based activity assays (Supplementary Figs. 12A, 13A, Fig. 3e; and Supplementary Table 3). Inset: Partial sequence alignment of the Rab32 subfamily and Rab23. Gray: Residues mutated to the corresponding Rab23 moiety; arrows: GtgE cleavage site (see also Supplementary Fig. 1). d Catalytic efficiency of GtgE mutants with Rab32 wild type. Identical experimental setup as in panel c (Fig. 3e, Supplementary Figs. 12B, 13B, and Supplementary Table 3)