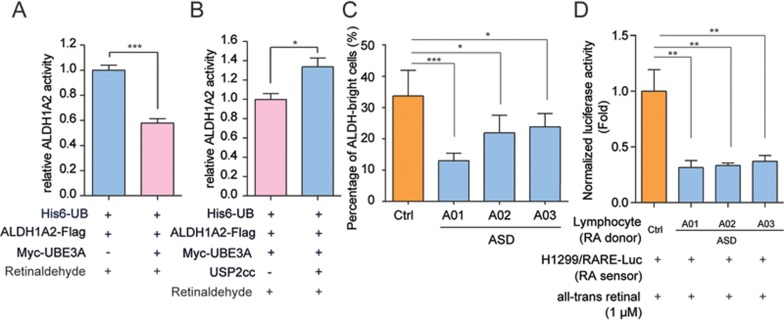
Figure 3.
UBE3A-mediated ubiquitylation suppresses the retinaldehyde dehydrogenase activities of ALDH1A. (A, B) UBE3A-conjugated poly-Ub chains on ALDH1A2 reduced its dehydrogenase activity toward retinaldehyde. ALDH1A2-Flag protein was enriched from HEK-293FT cells (A), followed by USP2cc treatment or not to remove the poly-Ub chains (B). The enriched ALDH1A2 protein was then subjected to dehydrogenase activity assays using all-trans retinaldehyde as the substrate. Relative dehydrogenase activity of polyubiquitylated ALDH1A2 protein was shown after normalization to that of the control group (A: n = 4; B: n = 3). Data were shown in means ± SEM. (C, D) Total cellular ALDH1A activities of the immortal lymphocytes from the autistic groups were significantly lower than that of the healthy control (multiple healthy lymphocytes cell lines), according to AldeFluor assay (C) or RARE-luciferase reporter assay (D). (C) The percentages of ALDH-bright cells were recorded after pre-setting DEAB (N,N-diethylaminobenzaldehyde)-treated cells for negative gating in flow cytometry. Values were expressed as means of quintuplicates of each individual ± SEM. (D) RA production in the immortal lymphocytes derived from the healthy control or autistic probands was assayed by co-culturing them (RA donor cells) with H1299 cells that bore RARE-luciferase reporter constructs (RA sensor cells). Cellular luciferase activities were assayed after 1 μM all-trans retinal treatment for 8 h, and normalized to control group (healthy lymphocytes). Values were expressed as means of quadruplicates of each individual ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; two-tailed t-test (A, B), one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's post hoc test (C, D).