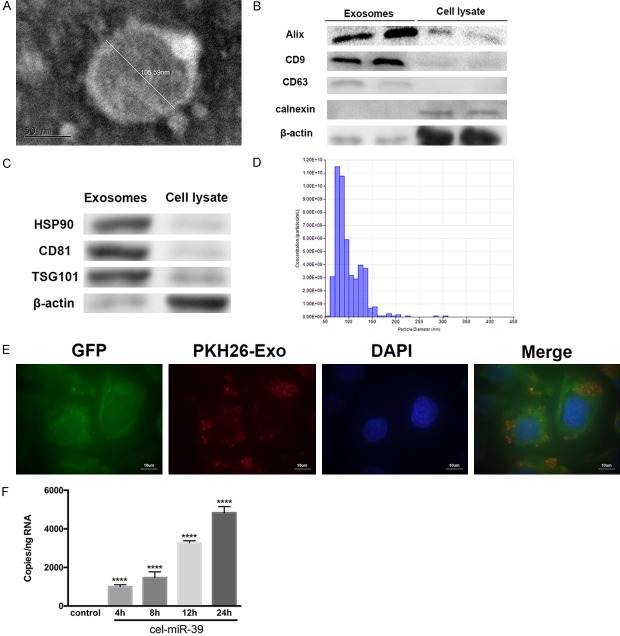
Figure 4.
Isolation of exosomes from telocytes (TCs) and investigation of their uptake by endothelial cells (ECs). A. Representative electron microscopy image of TC exosomes. The diameter of this exosome was measured to be 105.59 nm. Scale bar: 50 nm. B, C. To confirm their identity, exosomal preparations were compared with cells lysates by Western blotting. The blot shown an enrichment of the exosomal markers Alix, CD9, CD63, HSP90, CD81 and TSG101 but the absence of calnexin, an endoplasmic reticulum protein. β-actin was used as a loading control. D. Exosome identity was further confirmed with a qNano analysis, which measured the diameters of the particles with respect to concentration. Most particles ranged from 50 to 150 nm in diameter. E. Isolated exosomes from TCs were labeled with PKH26 (red) and added to the culture medium of GFP-labeled ECs (green). After 12 h, cells were stained with DAPI (blue) to label cell nuclei and confocal imaging showed that the exosomes were present in the cytoplasm of ECs. Scale bar: 10 µm. F. TCs were transfected with cel-miR-39 or left un-transfected (control). Cultured ECs were then treated with exosomes isolated from control or cel-miR-39-transfected TCs for the indicated times. The RNA levels of cel-miR-39 were then measured in ECs using RT-PCR. ****, P < 0.0001 versus control; n = 5.