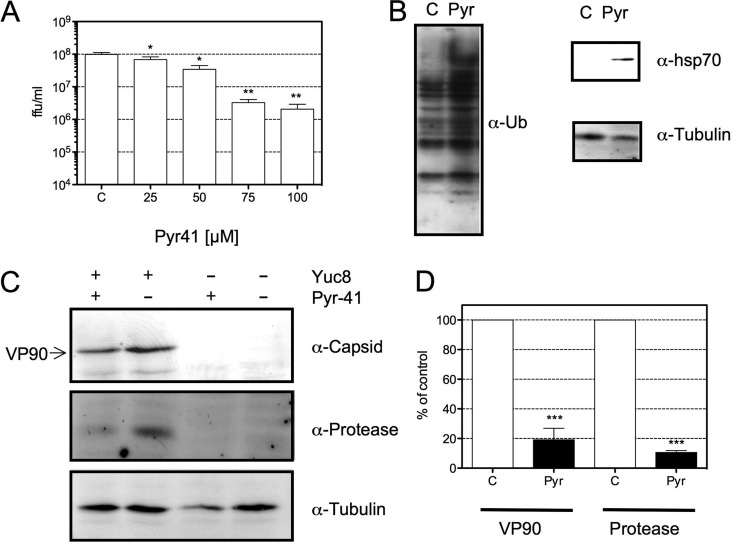
FIG 4.
Pyr-41, an inhibitor of E1-activating enzymes, reduces viral progeny production and the synthesis of viral proteins. C2Bbe1 cells were infected with HAstV Yuc8 at an MOI of 3. At the end of the adsorption period, Pyr-41 was added at the indicated concentrations, and cells were then processed at 18 hpi. (A) Cells and medium were collected together, and the titer of the viral progeny produced was evaluated. The data are expressed as focus-forming units per milliliter and represent the means of results from three independent experiments performed in duplicate ± standard errors of the means. *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01. (B) Yuc8-infected C2Bbe1 cells were incubated for 18 h with 100 μM Pyr-41 (Pyr) or dimethyl sulfoxide (C). Total proteins collected in Laemmli buffer were resolved by SDS-PAGE and transferred onto nitrocellulose membranes for detection of the indicated proteins. (C) Western blot analysis of the indicated proteins from infected or mock-infected cells in the presence or absence of 100 μM Pyr-41. The proteins were collected in Laemmli sample buffer, resolved by SDS-PAGE, transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane, and stained with the indicated antibodies. Immunodetection was performed by using Alexa 647-conjugated secondary antibodies. (D) Quantification of normalized values (using tubulin as a loading control) of expression for the indicated viral proteins in infected dimethyl sulfoxide (C)- or Pyr-41-treated cells. Data are expressed as a percentage of values for the control (dimethyl sulfoxide-treated cells) and represent the means ± standard errors of the means of results from five independent experiments. ***, P < 0.001.