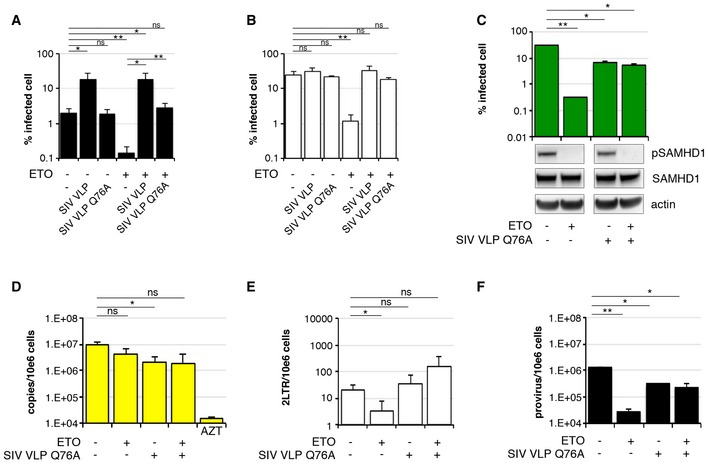
Figure 3. Vpx Q76A rescues DNA damage‐induced block to HIV‐1 infection.
-
A, BMDM were treated with 5 μM ETO for 18 h and co‐infected in the presence of ETO with VSV‐G HIV‐1 GFP and SIVmac virus‐like particles containing Vpx wild‐type (WT)/Vpr or Vpx Q76A mutant/Vpr (SIV VLP Q76A) (n = 3, mean ± s.e.m.; *P‐value ≤ 0.05; **P‐value ≤ 0.01; (ns) non‐significant, paired t‐test). (A) MDM were differentiated and cultured in human serum instead of FCS. (B) MDM were differentiated and cultured in FCS. A standard culture condition used in all experiments. See Materials and Methods.
-
C–FMDM were treated with 5 μM ETO for 18 h and co‐infected in the presence of ETO with HIV‐1 BaL and SIV VLP Q76A. DNA was isolated 18 h post‐infection for qPCR quantification of (D) late RT products; (E) 2LTR circles; (F) integrated viral DNA (n = 3, mean ± s.e.m.; *P‐value ≤ 0.05; **P‐value ≤ 0.01; (ns) non‐significant, paired t‐test). (C) The percentage of infected cells was quantified by the automated cell‐imaging system Hermes WiScan and ImageJ 48 h post‐infection. Cells from a representative donor were used for immunoblotting. (D) Late viral RT products. AZT: MDM treated with 20 μM AZT, a reverse‐transcriptase inhibitor, were used as control. (E) 2LTR circles. (F) Integrated copies of viral DNA, Alu‐Gag qPCR.
Source data are available online for this figure.
