-
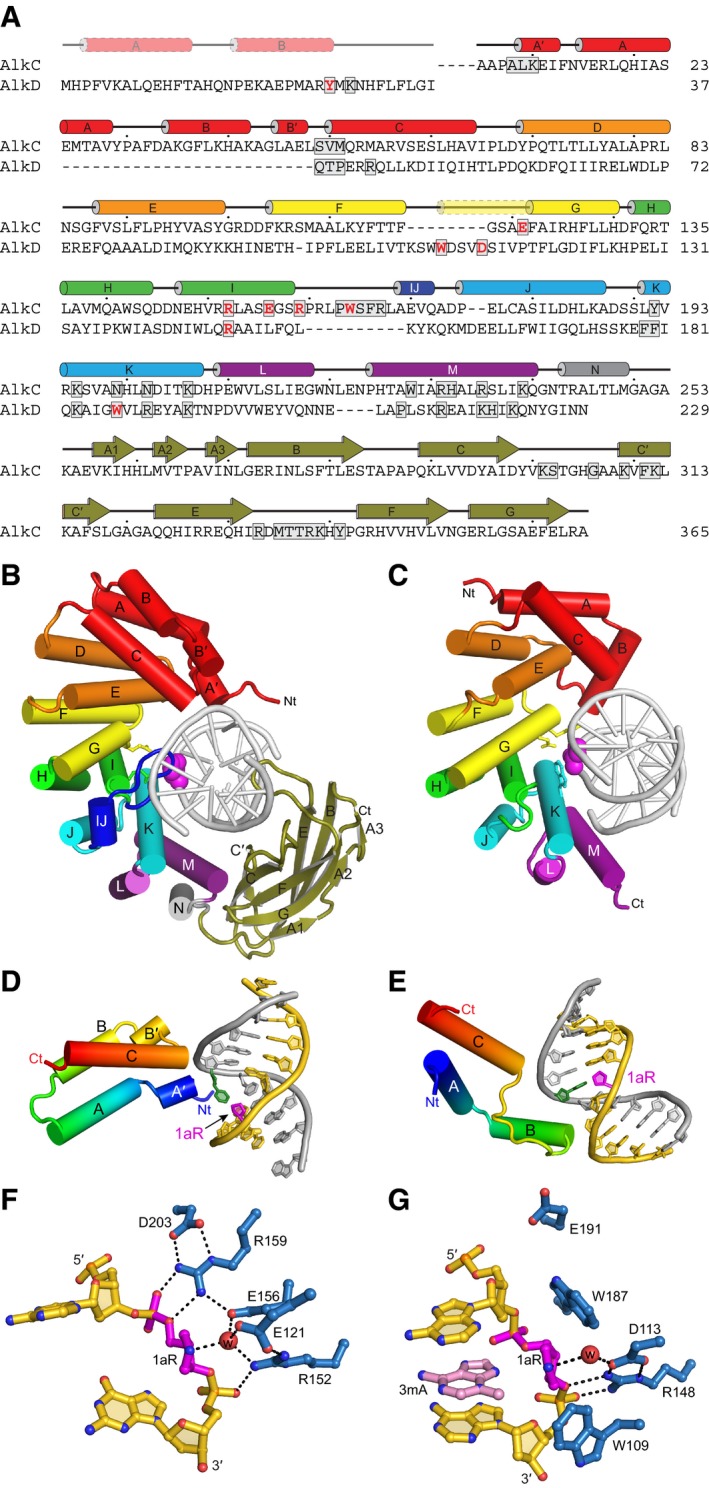
A
Structure‐based sequence alignment of PfAlkC and BcAlkD. Active site residues are red and DNA‐interacting residues are boxed. Secondary structures derived from the crystal structures are shown above the sequences. The transparent N‐terminal segment of helix αG (yellow) is unique to AlkD and helix αIJ (dark blue) is unique to AlkC.
-
B, C
Crystal structures of 1aR‐DNA complexes of PfAlkC (B) and BcAlkD (C, PDB ID 5CLD). The N‐terminal helical bundles are red; HEAT‐like repeats are orange, yellow, green, cyan, and purple; and the Ig‐like domain of AlkC is olive. Side chains of active site residues are shown as sticks, and the 1aR moieties are shown as magenta spheres.
-
D, E
Interactions between the N‐terminal helical bundles of PfAlkC (D) and BcAlkD (E) and DNA. Protein is colored rainbow from N‐ (blue) to C‐terminus (red). DNA strands are colored gold and silver, and 1aR and opposite thymine are magenta and green, respectively.
-
F, G
Active sites of PfAlkC (F) and BcAlkD (G). Protein residues are colored blue, DNA gold, 1aR magenta, and 3mA nucleobase pink. The catalytic water is shown as a red sphere, and hydrogen bonds are depicted as dashed lines.