Figure 4. Processing of Sde2UBL promotes interaction of Sde2‐C with the spliceosomal factors.
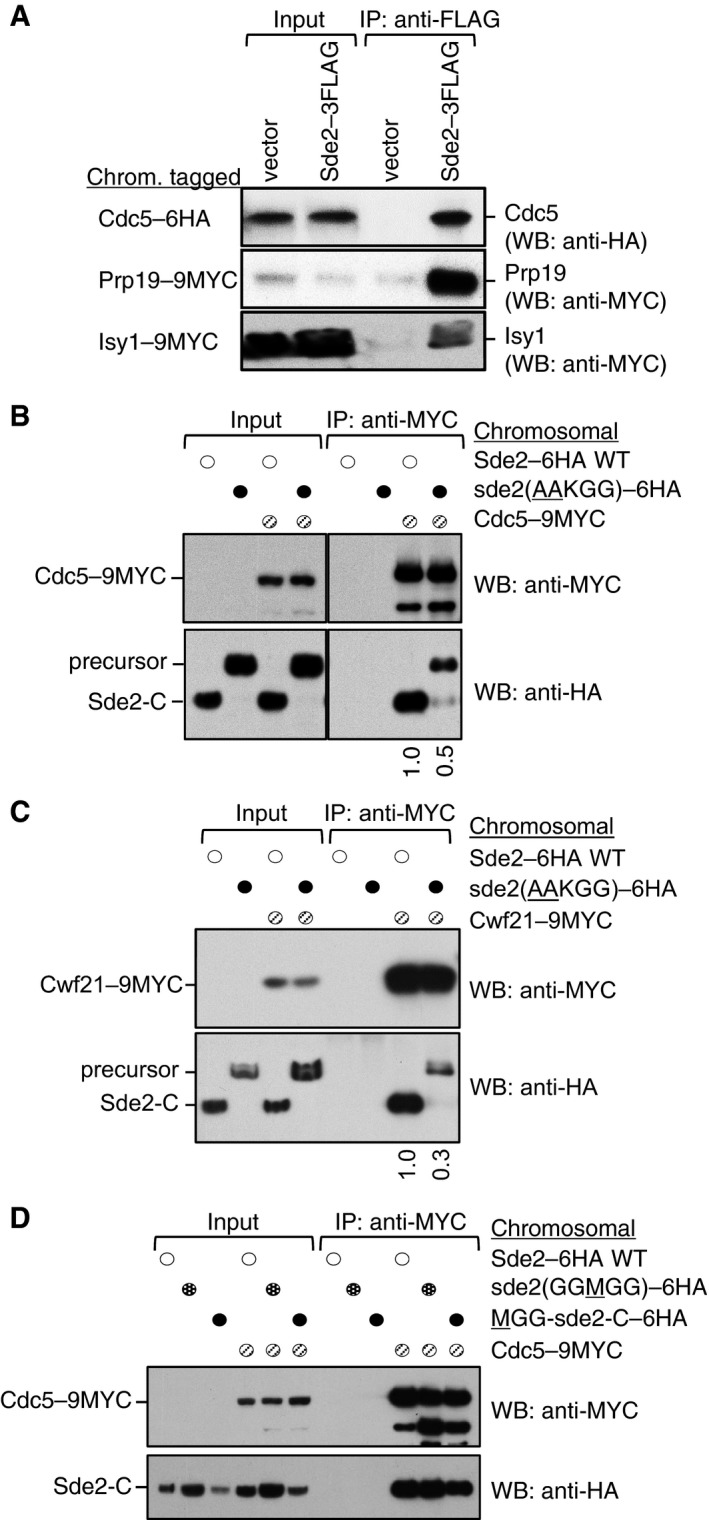
- Sde2 interacts with the spliceosomal Prp19 complex factors Cdc5, Prp19 and Isy1 in vivo. sde2 gene was 3FLAG‐tagged, and cdc5–6HA, prp19–9MYC and isy1–9MYC genes were tagged chromosomally.
- Co‐IP assay to monitor association of the processing‐defective Sde2 with Cdc5. Experiments are performed with proteins expressed at their endogenous levels by using chromosomally tagged strains with given epitopes at the C‐termini of indicated genes. IP was performed using anti‐MYC agarose resins followed by immunoblot assays with anti‐MYC antibody to monitor IP efficiency of Cdc5, and with anti‐HA antibody to monitor Co‐IP of Sde2 versions. Numbers below anti‐HA blot indicate ratio of Sde2 to Cdc5 (HA/MYC) signals obtained from ImageJ quantification of immunoblot signals. Cdc5 association of the processing‐defective Sde2 precursor is diminished to half.
- Co‐IP assay to monitor association of the processing‐defective Sde2 with Cwf21. Assay is similar to (B). Cwf21 association of the processing‐defective Sde2 precursor is diminished to one‐third.
- Co‐IP assay to monitor association of MetSde2‐C with Cdc5. Assay and quantitation is similar to (B). MetSde2‐C generated from processing of GGMGG mutant precursor or after translation de novo does not show obvious defects in spliceosomal association.
Source data are available online for this figure.
