Figure 4.
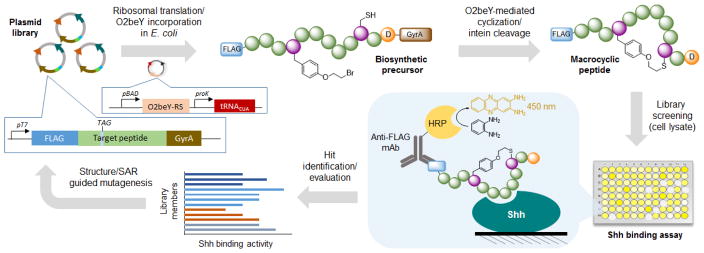
Overview of strategy for evolution of macrocyclic peptides. A plasmid library encoding for partially randomized peptide sequences fused to a FLAG tag and a C-terminal GyrA intein are transformed into E. coli cells and arrayed on multiwell plates. The corresponding pre-cursor polypeptides are produced via ribosomal translation and O2beY incorporation via amber stop codon (TAG) suppression. The macro-cyclic peptides are produced inside cells through ‘self-processing’ of the biosynthetic precursors via O2beY/Cys cyclization and aspartate-induced intein cleavage. After cell lysis, peptide binding to immobilized Shh is quantified colorimetrically. The variants showing improved Shh binding activity are deconvoluted via DNA sequencing. The best variant and acquired SAR data are used for the next round of affinity maturation.