Fig. 4.
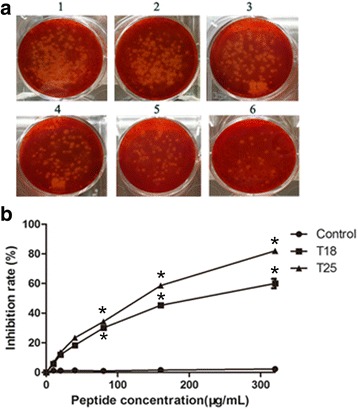
Inhibition of peptide T18 and T25 to plaque production on Vero cells. a Inhibition ability of synthetic peptides T25 was determined by the reduce plaque assay. 100 TCID50/0.1 mL BEFV and 2-fold serial diluted synthetic peptides ranging from 10 μg/mL to 320 μg/mL were pre-inoculated and then inoculated Vero cells.1, BEFV; 2, BEFV + 20 μg/mL;3, BEFV + 40 μg/mL; 4, BEFV + 80 μg/mL; 5, BEFV + 160 μg/mL; 6, BEFV + 320 μg/mL. b Synthetic peptides T18 and T25 at 2-fold serial dilution concentrations of 10-320 μg/mL were incubated with 100 TCID50/0.1 mL BEFV, respectively. The synthetic irrelevant peptide (AEMLELS) acted as control. Antiviral activities of the peptides were determined by calculating the percentage of inhibitory rate compared against the controls using the following formula; IN (%) = T/C × 100 [42], where, T is the mean of the number of plaque treated with different concentration of peptides. C is the mean of the number of plaque treated with corresponding synthetic irrelevant peptides that did not react with G1 protein. Data presented were the mean OD values (±SD) of triplicate samples. Figures were performed using the GraphPad™ Prism 5.0 software. Statistical significance (p < 0.05) was noted by “*” compared to control groups
