Fig. 1.
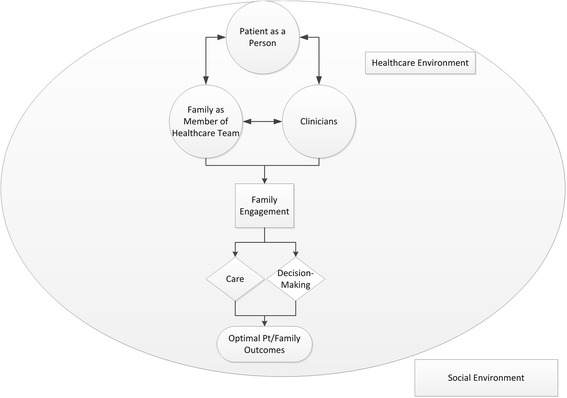
Conceptual model of family engagement in the intensive care unit (ICU). Many factors impact medical decisions for a patient. Patient factors include the patient as a person and their medical condition. Patient as a person represents the person’s prior experiences, values, preferences and goals. Environmental factors include the health care environment situated within a larger societal context. Family members may engage in care or decision-making. The family’s role in care gives purpose in crisis and may help family members cope with the exposure to critical illness. Their direct participation may also improve patient adherence to treatment plan and attainment of treatment goals. In shared decision-making the family is engaged as a member of the health care team. The family is typically most familiar with the patient as a person and the patient’s past health status. The clinicians are typically most knowledgeable of the patient’s critical illness. The decision-support intervention is designed to facilitate communication between the family and clinicians about the patient as a person and their medical condition. Family engagement in this manner facilitates a shared medical decision that is consistent with the patient’s values and goals in the context of their illness experience and medical condition, and is congruent with what the patient would choose if they were competent to make such a decision. Thus, we hypothesize that family engagement can influence family response to critical illness, and also the treatment plan. Ultimately, both patient and family outcomes are optimized
