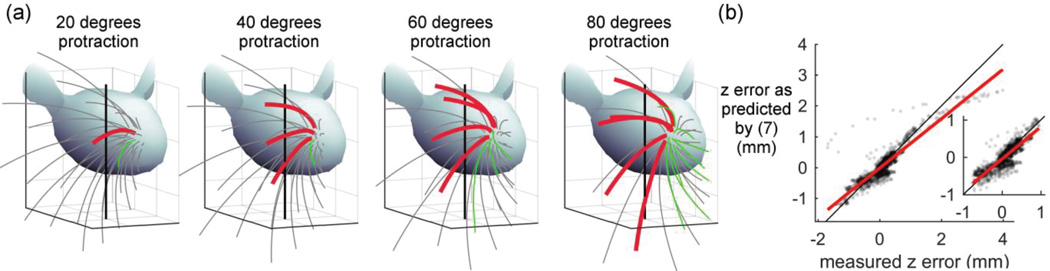
Fig. 4. Edge mode (frictionless) simulations can be used to predict how multiple whiskers will slip against a peg and to place error bounds on the resulting contact point location.
(a) Four frames from Supplementary Video 3, which simulates a rat whisking against a vertical peg. Thick red whiskers are those currently in contact with the peg, and green whiskers are those that came in contact with the peg and subsequently pushed past it. Light gray whiskers never contact the peg. (b) The measured distance in contact point location between edge and contact point mode (zerror) is well predicted by equation (7). This equation thus allows error bounds to be placed on the contact point location calculated during simulations using edge mode. The dots are semi-transparent to show the data density. The inset excludes outliers as defined in the text. Measured zerror ranges between −0.76 and 0.96 mm, and predicted zerror ranges between −1.0 and 1.1 mm. In both Fig. 4b and the inset the identity line is plotted in black and the best fit line is plotted in red (see text for equations).