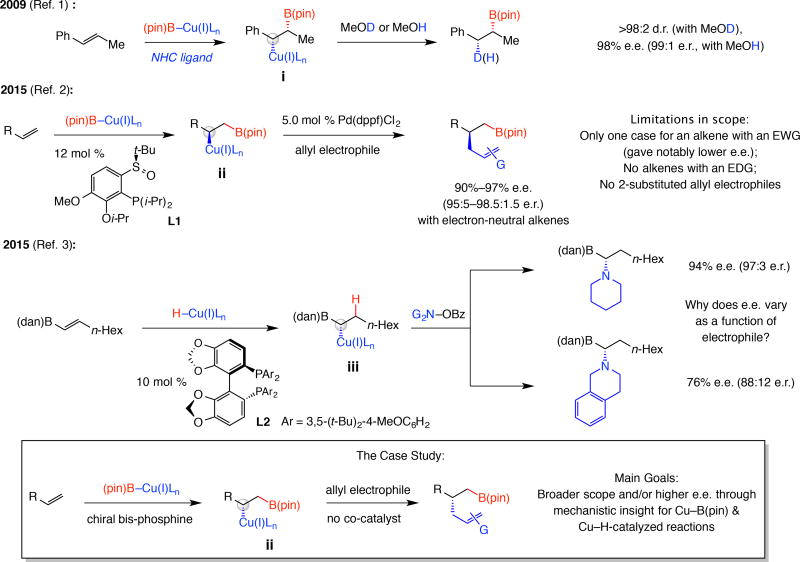
Figure 1. Key problems and the goals of this study.
Despite significant advances, notable questions remain unanswered. Cu–B(pin) addition to aryl alkenes is site- and syn-selective and the Cu-alkyl species can react in situ with an allyl electrophile. However, reactions require high ligand loading and a precious metal co-catalyst and scope is limited. Transformations involving Cu-H additions have also been developed, where enantioselectivities can vary widely, depending on electrophile identity despite organocopper formation being stereochemistry determining. With development of a catalytic site- and enantioselective boron-allyl additions as the model study, several key mechanistic issues will be examined that allow for scope of the reactions to be expanded considerably. NHC, N-heterocyclic carbene; Ln, ligands; e.r., enantiomeric ratio; pin, pinacolato; dppf, 1,1’-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene; EWG, electron withdrawing group; EDG, electron donating group; dan, 1,8-diaminonaphthalene; Bz, benzoyl; G, functional group.