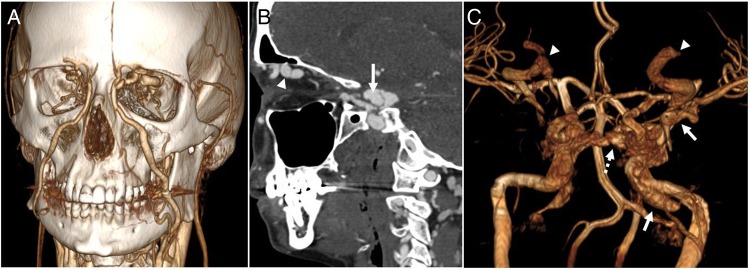
Figure 2.
(A) Three-dimensional surface reconstruction of a CT angiogram of the head and neck demonstrates dilated bilateral superior ophthalmic veins draining to the angular and facial veins. (B) Sagittal CT angiography demonstrates a pseudoaneurysm of the left internal carotid artery (arrow) which communicates with the left cavernous sinus consistent with a direct carotid–cavernous fistula. (C) Surface reconstruction of a pre-intervention MR angiogram shows abnormal opacification of the left cavernous sinus and tributaries including the intercavernous sinus (dotted arrow) to the contralateral cavernous sinus, left sphenoparietal sinus and left sylvian vein (arrow), and bilaterally dilated superior ophthalmic veins (arrowheads). Also note a large unruptured pseudoaneurysm at the left petrous segment of the internal carotid artery (arrow).