Figure 1.
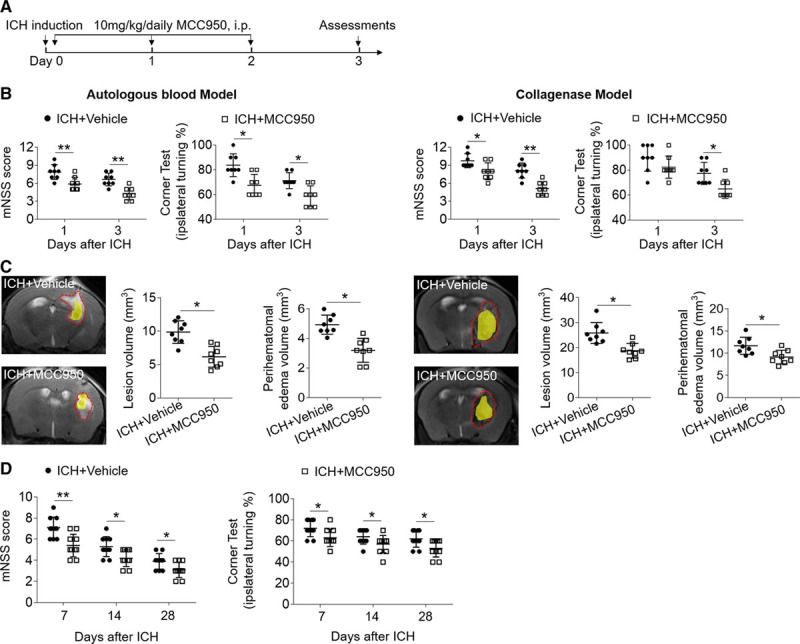
MCC950 attenuates brain injury and improves long-term outcome after intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH). ICH was induced in C57BL/6 mice by injection of autologous blood or collagenase. A, Flow chart illustrates MCC950 administration and experimental design. Mice received daily intraperitoneal (IP) injections of MCC950 (10 mg/kg) or an equal volume of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) vehicle for 3 consecutive days starting immediately after ICH induction. B, Neurological tests were performed to evaluate the motor, sensory, and balance functions in mice receiving vehicle or MCC950 at days 1 and 3 after injection of autologous blood (left) or collagenase (right). C, T2-weighted image (T2WI) sequences were scanned to assess lesion volume at day 3 after ICH induced by injection of autologous blood (left) or collagenase (right), as outlined in red. Susceptibility-weighted sequences were assessed for hematoma lesion volume, visible in yellow regions. Quantification of lesion volume and perihematomal edema in mice receiving MCC950 or vehicle at day 3 after ICH induced by injection of autologous blood (left) or collagenase (right). n=8 mice per group. D, Mice received vehicle or MCC950 at a dose of 10 mg/kg by intraperitoneal injection. The assessments of modified Neurological Severity Score (mNSS) score and corner test were performed at days 7, 14, and 28 after ICH induced by injection of collagenase. n=10 per group. Data are presented as mean±SD. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
