Figure 3.
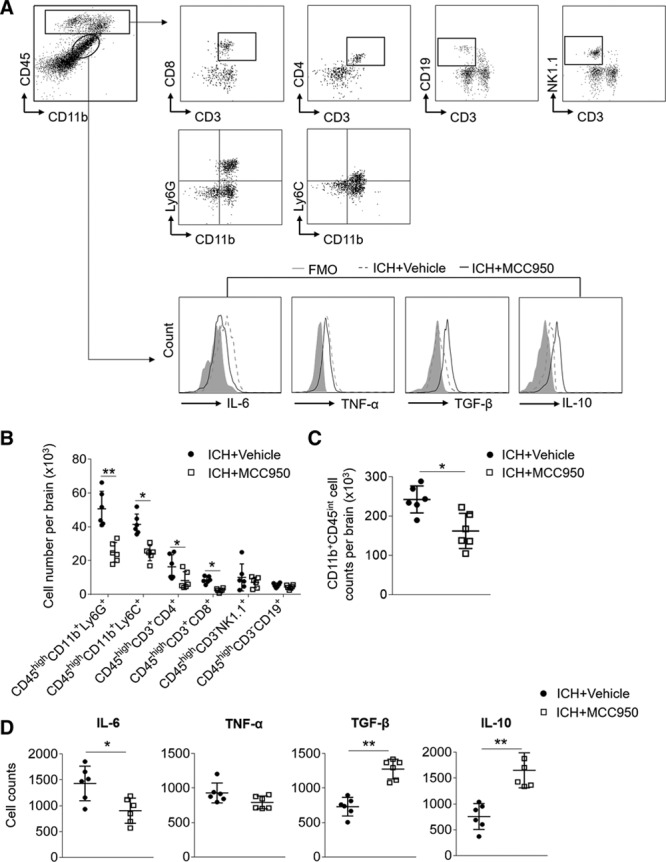
MCC950 reduces leukocyte infiltration and microglia production of proinflammatory factors after intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH). ICH was induced in C57BL/6 mice by injection of autologous blood. Mice received daily intraperitoneal (IP) injections of MCC950 (10 mg/kg) or an equal volume of vehicle for 3 consecutive days starting immediately after ICH induction. At day 3 after ICH, immune cells were isolated from brain tissues of ICH mice receiving MCC950 or vehicle. A, Gating strategy of brain-infiltrating immune cells including CD4+ T cells (CD3+ CD4+), CD8+ T cells (CD3+ CD8+), B cells (CD3−CD19+), NK cells (CD3−NK1.1+), monocyte/macrophages (CD11b+CD45highLy6C+), neutrophils (CD11b+CD45highLy6G+), and microglia (CD11b+CD45int) and their expression of IL (interleukin)-6, TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor-α), TGF-β (transforming growth factor-β), and IL-10. FMO, fluorescence minus one. B, Data points show counts of brain-infiltrating leukocytes in the brains of ICH mice receiving indicated treatment. C, Data points show counts of microglia in the brains of ICH mice receiving indicated treatment. D, Data points show the counts of microglia expressing IL-6, TNF-α, TGF-β, and IL-10 in the brains of ICH mice receiving indicated treatment. n=6 mice per group. Data are presented as mean±SD. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
