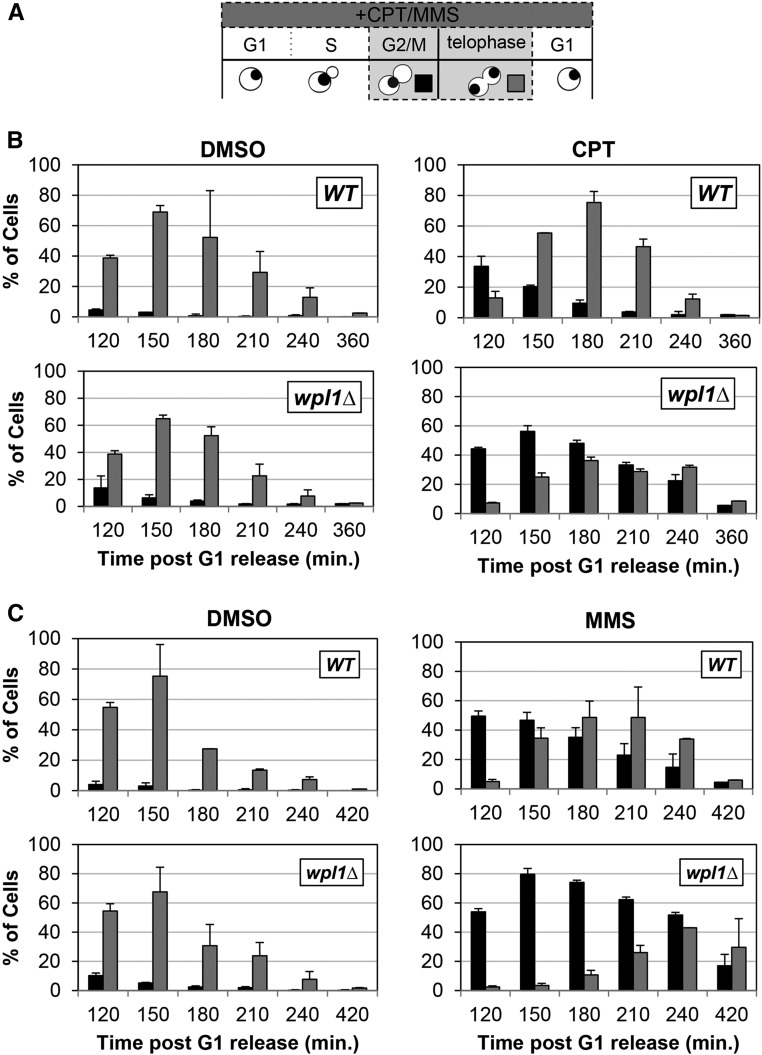
Figure 2.
Wpl1p promotes recovery from G2/M delays generated by exposure to the DNA-damage-inducing agents camptothecin (CPT) and MMS. (A) Schematic of time course and analysis of cell cycle progression for untreated and CPT- or MMS-treated cells in (B and C). Wild-type (WT) (VG3349-1B) and wpl1∆ (VG3360-3D) cells were grown to midlog phase in YPD at 23°, arrested in G1 by addition of α-factor, then released from G1 into YPD (Materials and Methods). At the time of release from G1, cells were split into two aliquots: either CPT (final 20 µg/ml) or MMS (final 0.01%) was added to one and DMSO was added to the other. Once most cells had entered S-phase (90 min after release from G1), α-factor was added to ensure cells would progress through one cell cycle and rearrest in G1. Aliquots were taken every 30 min and fixed in 70% ethanol. Fixed cells were stained with DAPI to detect chromosomal DNA for scoring. Cells were scored for bud morphology (unbudded, small–medium bud, or large bud) and whether they contained a single DAPI chromosomal mass or two DAPI masses. (B) wpl1∆ cells grown in the presence of CPT from G1 onward exhibit a prolonged mitotic delay. WT (VG3349-1B) and wpl1∆ (VG3360-3D) cells were synchronously released from G1, as described (A), in YPD media buffered with 25 mM HEPES pH 7.4 containing DMSO alone or with 20 µg/ml CPT (Materials and Methods). Graphs show the percentage of large-budded cells with a single DNA mass (G2/M; black) or two DNA masses (telophase; gray). (C) wpl1∆ cells grown in the presence of MMS from G1 onward exhibit a prolonged mitotic delay. WT (VG3349-1B) and wpl1∆ (VG3360-3D) cells were synchronously released from G1, as described in (B), except that YPD media (unbuffered) contained DMSO alone or 0.01% MMS. Cells were collected, processed, and scored as described in (A). Graphs show the percentage of large-budded cells with a single DNA mass (G2/M; black) or two DNA masses (telophase; gray).