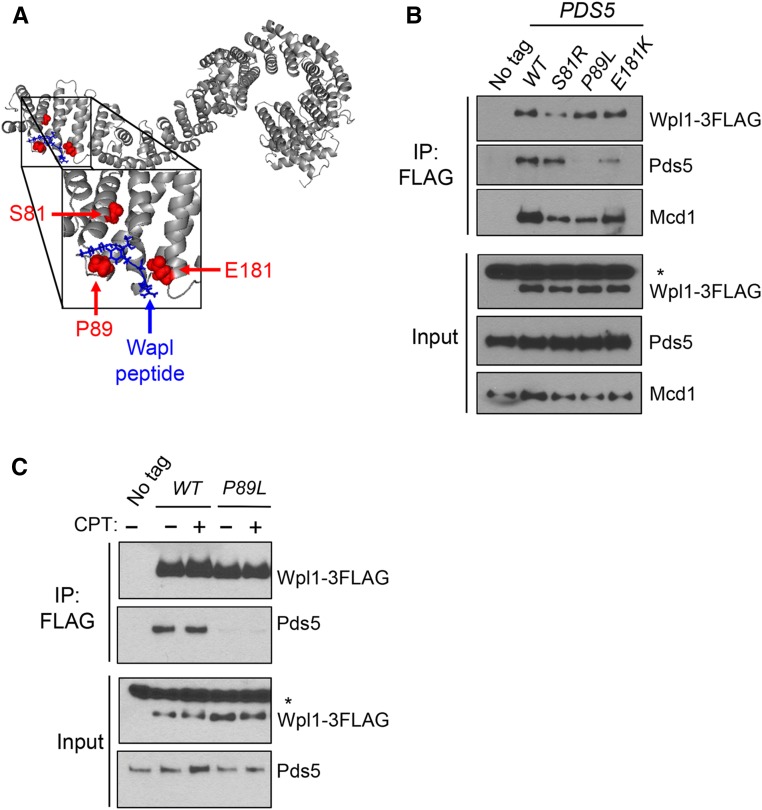
Figure 6.
Pds5p N-terminus promotes Wpl1p binding to the cohesin complex. (A) Crystal structure of Pds5B bound to the YSR motif of Wapl from Ouyang et al. (2016). Gray: Pds5B; blue: Wapl peptide; red: eco1-ts suppressors from Rowland et al. (2009) and Sutani et al. (2009). Yeast residues were mapped to analogous residues on Pds5B through alignment. (B) Pds5p N-terminal mutants impair Wpl1p’s binding to cohesin and but have different effects on Wpl1p’s interaction with Pds5p. Wpl1p-3FLAG was immunoprecipitated from protein extracts in asynchronous cultures containing Wpl1p-3FLAG and either PDS5 (MSB192-2A), pds5-S81R (MSB193-1B), pds5-P89L (MSB194-1C), or pds5-E181K (MSB195-2D), as described in the Materials and Methods. No tag control contains wild-type (WT) untagged WPL1 and PDS5 alleles (VG3349-1B). For western blot analysis, Wpl1p was detected using mouse anti-FLAG, Pds5p was detected using rabbit anti-Pds5, and Mcd1p was detected using rabbit anti-Mcd1 antibodies (Materials and Methods). For anti-FLAG, a nonspecific species present in all cells is denoted by an asterisk. (C) Assessment of interaction between Wpl1p-3FLAG and Pds5p (MSB192-2A) or Pds5p-P89L (MSB194-1C) when treated with CPT. Asynchronous cultures were treated either with DMSO or 20 µg/ml CPT for 3 hr before being harvested. No tag control is the WPL1 PDS5 (VG3349-1B) strain, which was treated with DMSO. Immunoprecipitation (IP) and western blot analysis were performed as described in (B) and the Materials and Methods.