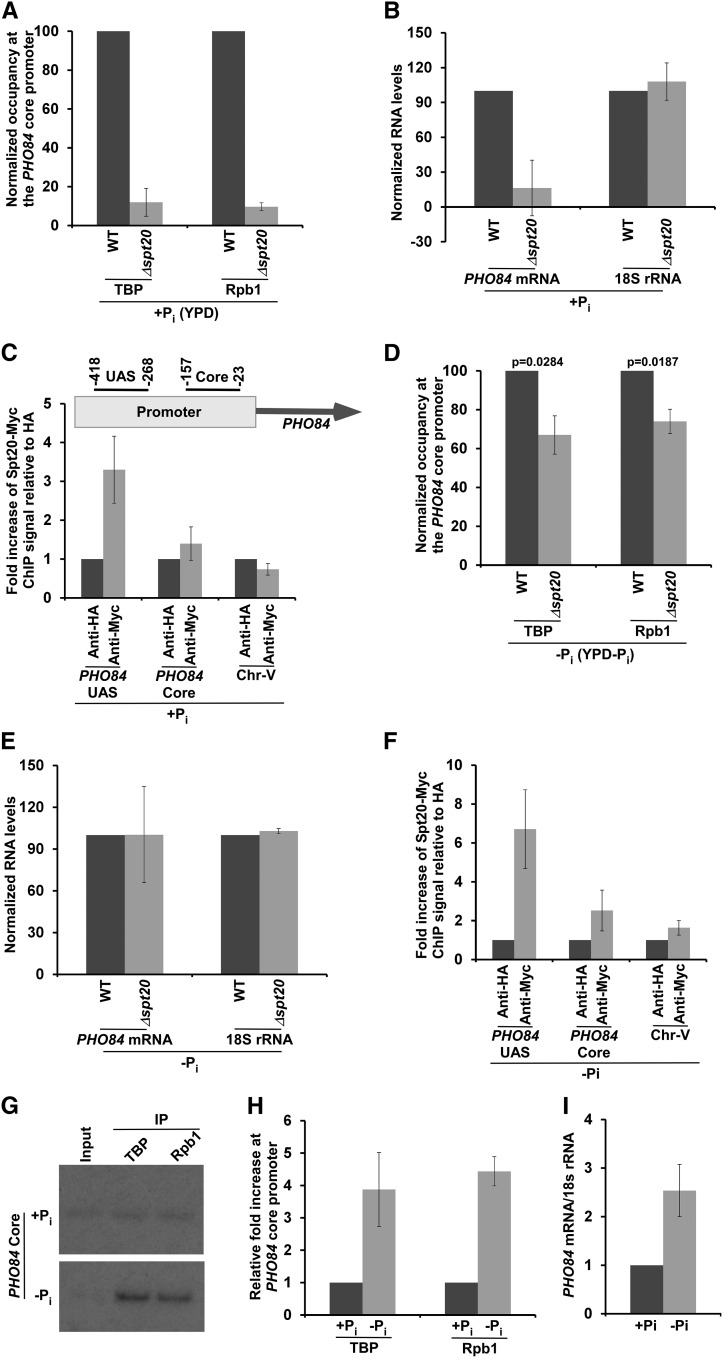
Figure 1.
SAGA is required for PIC formation at the PHO84 core promoter to initiate transcription in the presence of inorganic phosphate (Pi) in the growth medium. (A) ChIP analysis of TBP and RNA polymerase II (Rpb1) at the PHO84 core promoter in the Δspt20 and WT strains in the growth medium with Pi (i.e., YPD or +Pi). The ChIP signal of the WT strain was set to 100, and the ChIP signal of the mutant strain was normalized with respect to 100. (B) RT-PCR analysis of PHO84 mRNA and 18S rRNA levels in the WT and Δspt20 strains in YPD. (C) ChIP analysis for the recruitment of the Spt20 component of SAGA to the PHO84 promoter in YPD. Upper panel: Schematic diagram showing the locations of the primer pairs at the PHO84 promoter for ChIP analysis. The numbers are presented with respect to the position of the first nucleotide of the initiation codon (+1). (D) ChIP analysis of TBP and Rpb1 at the PHO84 core promoter in the Δspt20 and WT strains in the growth medium without Pi (i.e., YPD-Pi or –Pi). (E) RT-PCR analysis of PHO84 mRNA and 18S rRNA levels in the WT and Δspt20 strains in growth medium without Pi. (F) ChIP analysis for recruitment of the Spt20 component of SAGA to the PHO84 promoter in the absence of Pi in the growth medium. (G) ChIP analysis of TBP and Rpb1 at the PHO84 core promoter in the presence and absence of Pi in the growth media. (H) Results of (G) are plotted in the form of a histogram. (I) Relative PHO84 mRNA levels in the presence and absence of Pi in the growth media. ChIP, chromatin immunoprecipitation; Pi, inorganic phosphate; PIC, preinitiation complex; UAS, upstream activating sequence; WT, wild-type; Chr. -V, Chromosome V; and TBP, TATA-box binding protein.