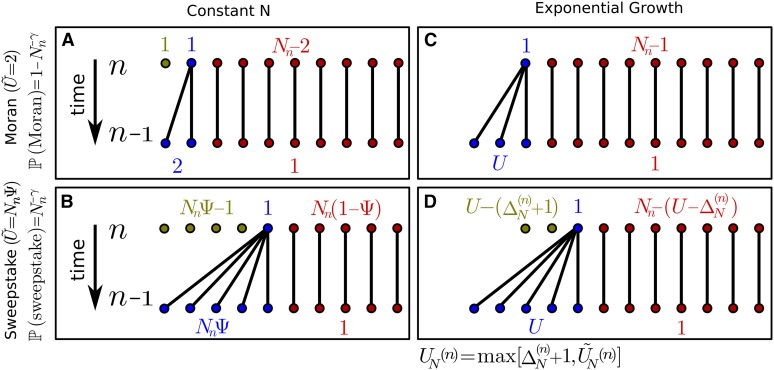
Figure 1.
Illustration of the extend Moran model with exponential growth. Shown are the four different scenarios of population transition within a single discrete time step. (A) The population size remains constant and a single individual produces exactly two offspring (“Moran-type” reproductive event). (B) The population size remains constant and a single individual produces offspring (“sweepstake” reproductive event). (C) The population size increases by individuals and a single individual produces exactly offspring. (D) The population size increases by individuals and a single individual produces exactly offspring. Note that n denotes the number of steps in the past, such that denotes the present. An overview of the notation used in this model is given in Table 1.