Figure 5. Computational modeling and X-ray assessment of the Arg29VHH–Glu67RTA interaction.
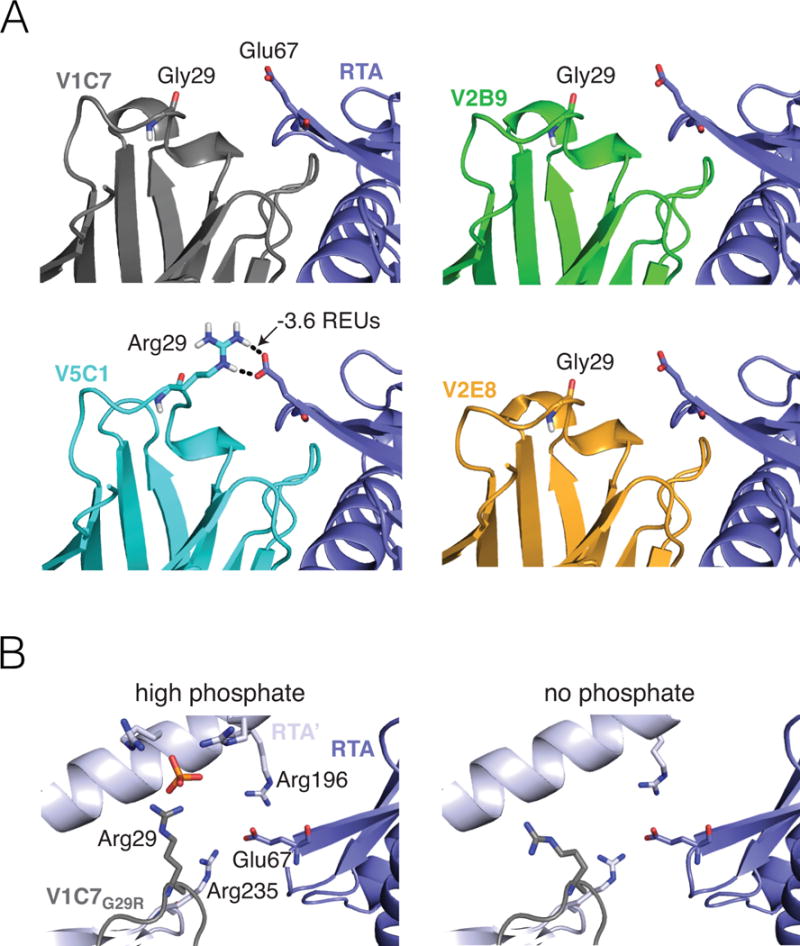
(Panel A) A representative computational model chosen by clustering the V5C1 ensemble by structural similarity has a favorable interaction of −3.6 REUs between Arg29V5C1 and Glu67RTA. Corresponding representative models for V1C7, V2B9, and V2E8 have no interaction between Gly29VHH and Glu67RTA. Broken lines indicate hydrogen bonds. (Panel B) Methodological artefacts prevent X-ray crystallography from confirming the importance of the Arg29VHH–Glu67RTA interaction in the V1C7G29R mutant. Crystallization in the presence of 1.6 M ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (left) causes Arg29VHH to interact with a phosphate molecule rather than Glu67RTA. Meanwhile, Glu67RTA engages two arginine residues (Arg196 and Arg235) from a symmetry-related RTA molecule (RTA’); this interaction is also observed under crystallization conditions devoid of phosphate (right).
