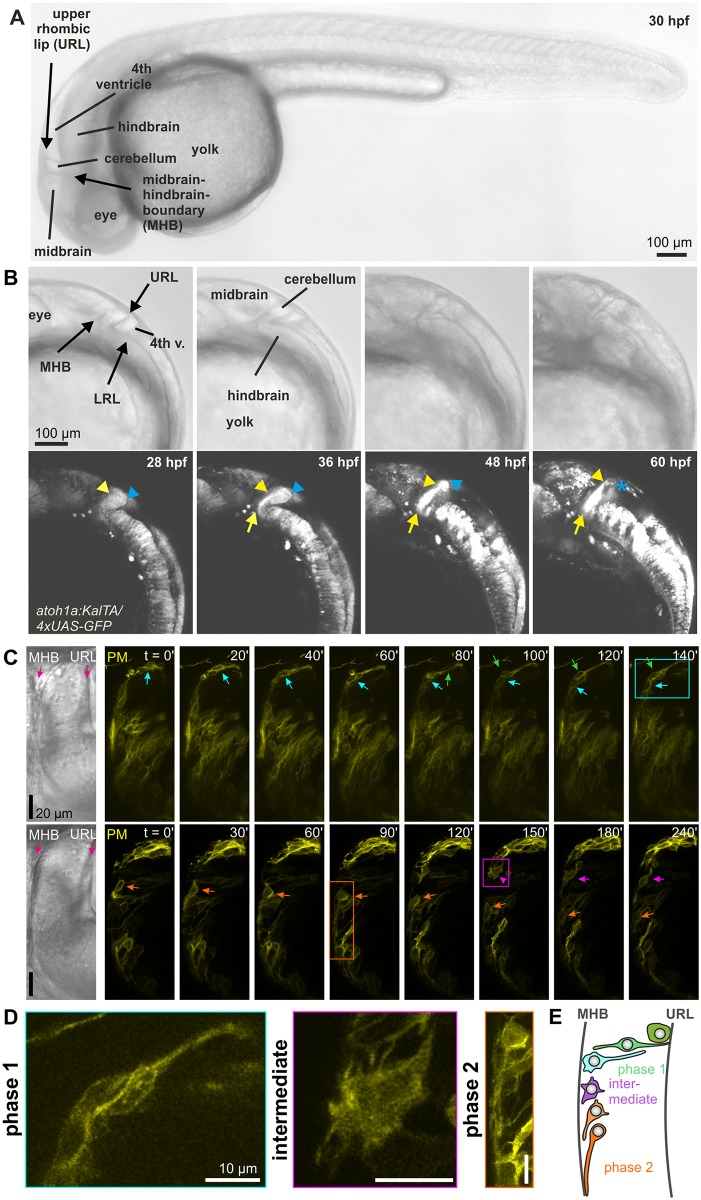
Fig 1. THNs migratory route and associated morphological changes.
(A) Anatomical overview of atoh1a:KalTA/4xUAS-GFP-expressing larvae from 30 hpf. Prominent features are indicated in transmitted-light images (top panel). Scale bar: 100 μm. For further details about THN position in adults, refer to [29]. (B) THNs are identified in the lower panel by their fluorescence and position in the cerebellum between URL and MHB, as well as their expression of GFP from an atoh1a promoter. Over time, cells migrate towards the MHB, which they follow ventrally to form a large cluster. Blue arrowheads and stars indicate start position, yellow arrowheads migrating THNs, yellow arrows point to the emerging THN cluster at the ventral end of the MHB. Anatomical features are indicated in the transmitted light images in the top row. Scale bar: 100 μm. See also S1 Video. (C) Morphologically, THNs begin their migration as very elongated cells that remain in contact with the URL until the main cell body has reached the MHB (arrows; top panel). At the MHB, dorsal cells exhibit a poorly polarized stage with many protrusions (arrowhead). Cells positioned more ventrally at the MHB assume a unipolar morphology with the protrusion extending ventrally (arrows). THNs transiently express PM-targeted YFP. Elapsed time is indicated at the top. Scale bar: 20 μm. Colored frames indicate the cells shown in (C). See also S2 Video. (D) Higher magnification of THNs indicated in (B), illustrating the morphological changes of THNs along their migratory route. Scale bar: 10 μm. (E) Schematic representation of THN morphology in different phases of migration. atoh1a; atonal 1a; GFP, green fluorescent protein; hpf, hours post fertilization; LRL, lower rhombic lip; MHB, midbrain-hindbrain boundary; PM, plasma membrane; THNs, tegmental hindbrain nuclei neurons; UAS, upstream activating sequence; URL, upper rhombic lip; YFP, yellow fluorescent protein.