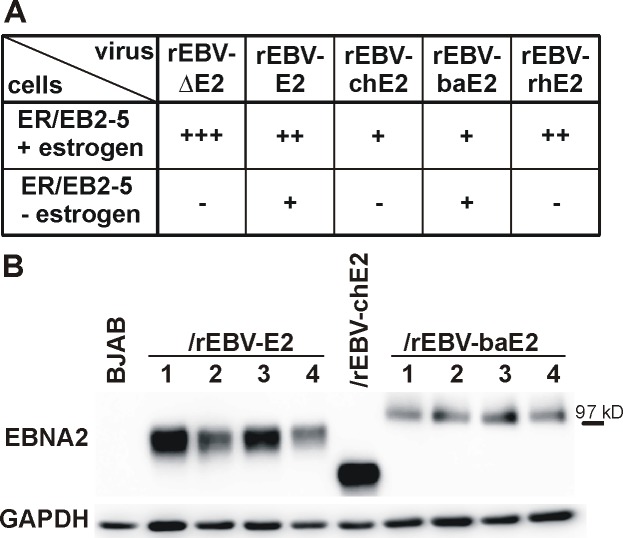
Fig 2. Maintenance of B cell immortalization in conditionally immortalized ER/EB2-5 cells by rEBVs.
A) ER/EB2-5 cells were infected with rEBVs and distributed into 100 microtiter wells. Half the wells were selected for infection by culture with medium containing puromycin and estrogen (+estrogen) and the other half of the cells underwent biological selection in medium without additives (-estrogen) to determine functionality of the EBNA2 protein. After 6 weeks the number of wells with cell growth was determined. The average result from multiple experiments is shown with 2 independent viral supernatants of each rEBV tested. +: 1–20 wells with growth/50 total wells, ++: 21-44/50, +++: 45-50/50, -: no growth. B) Four weeks after infection, selected clones growing in the absence of estrogen were used to detect EBNA2 and GAPDH as loading control by immunoblot. Cells infected with rEBV-E2, rEBV-chE2, or rEBV-baE2 express an EBNA2 species of the relative molecular weight expected for the respective rEBV.