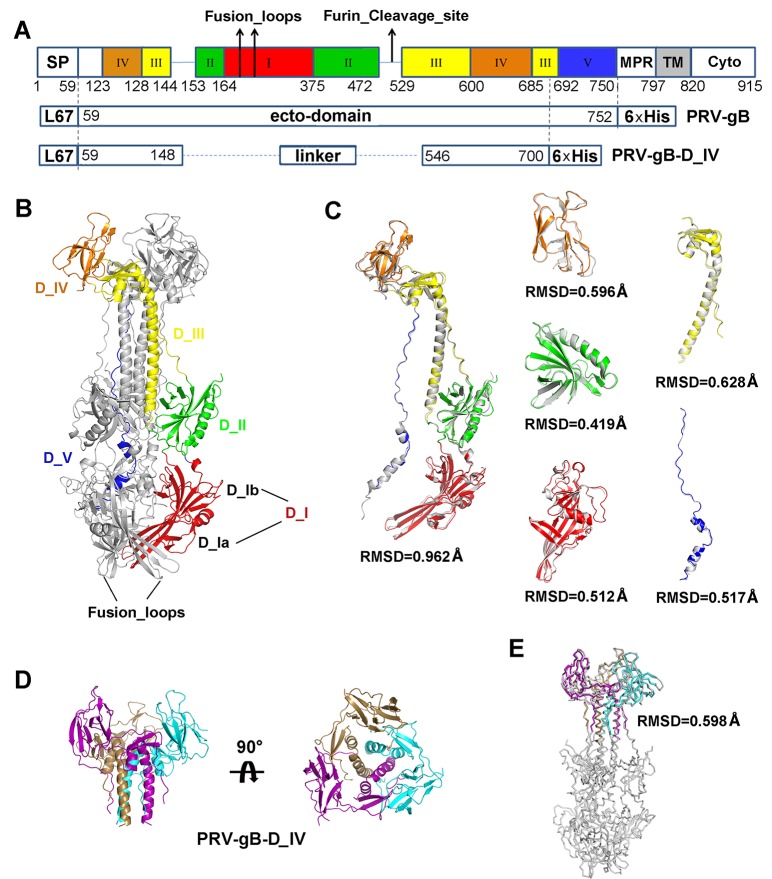
Fig 2. Crystal structure of PRV gB and gB-D_IV.
(A) Schematic representation of PRV gB architecture and the construct design of gB ectodomain and D_IV. Each domain is represented by different colors, and the positions of fusion loops and potential furin cleavage site are indicated by arrows. SP, signal peptide; MPR, most polymorphic region; TM, transmembrane region; Cyto, cytoplasmic tail; L67, signal peptide of gp67. (B) Overall structure of PRV gB trimer. One of the protomers is colored by domains as in (A) and labeled accordingly. The fusion loops are indicated by black arrows. (C) Superposition of PRV gB and HSV gB. The gB protomers and each individual domains are superimposed respectively. The rmsd values of Cα atom coordinates of aligned residues are shown under each comparison figure. (D) Crystal structure of PRV gB-D_IV, top and side views. The gB-D_IV exists as homotrimer and is colored by chains. (E) Structural alignment between the PRV gB trimer and D_IV.