Figure 6. BG and Ctx microglia show substantial variation in expression of genes associated with multiple functional families.
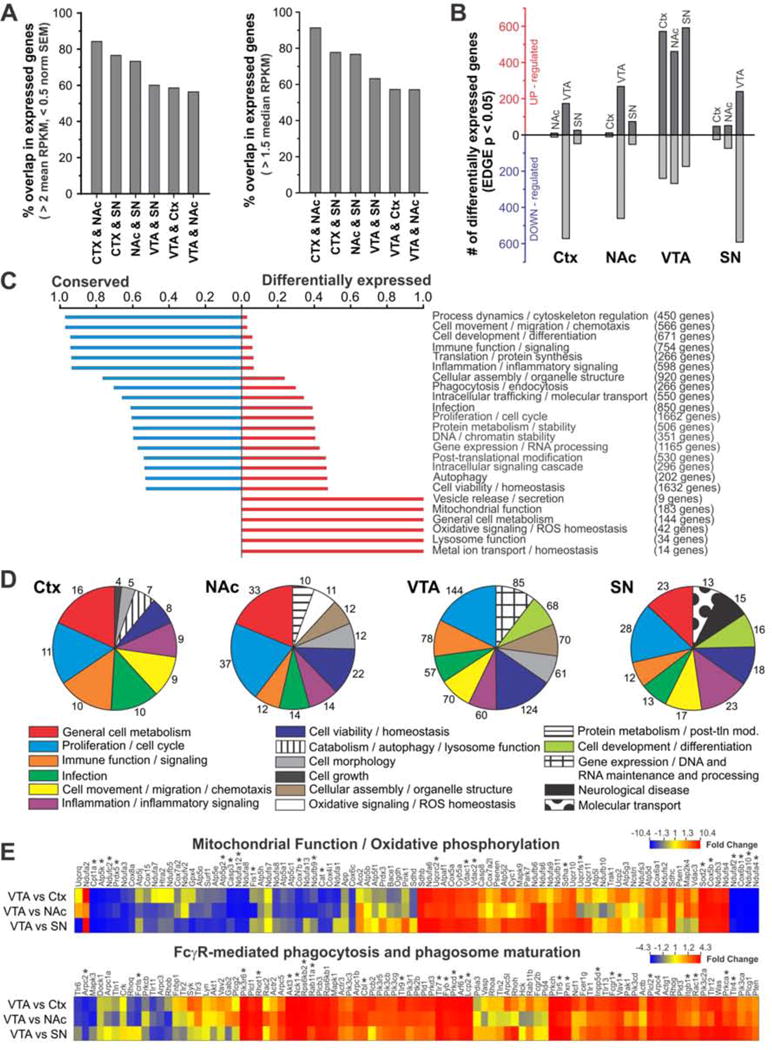
A – Degree of overlap in expressed genes in pairwise comparisons of BG and Ctx microglia using mean RPKM (left) or median RPKM (right) threshold for expression. B – Number of significantly up- and down-regulated genes in pairwise comparisons of BG and Ctx microglia. (EDGE P-value < 0.05; mean RPKM > 2 and norm. SEM < 0.5 in the more highly-expressing region). C – Degree to which genes in particular functional families are “conserved” (expressed by microglia in all regions) or “differentially expressed” (not expressed by microglia in all regions). D –Pie charts showing top 10 functional families in lists of genes that are significantly up-regulated in microglia in that region compared to microglia from at least one other region. Number of genes implicated in each functional family shown at perimeter. E – Key canonical signaling pathways altered in VTA microglia. Heat maps show all detected microglial genes involved in mitochondrial function/oxidative phosphorylation (top), and Fcγ-receptor mediated phagocytosis/phagosome maturation (bottom). Color scale represents fold change for pairwise comparisons listed at left. * Genes found to be significantly up-or down-regulated in VTA microglia compared to microglia from at least one other region. See also Figs. S5–6.
