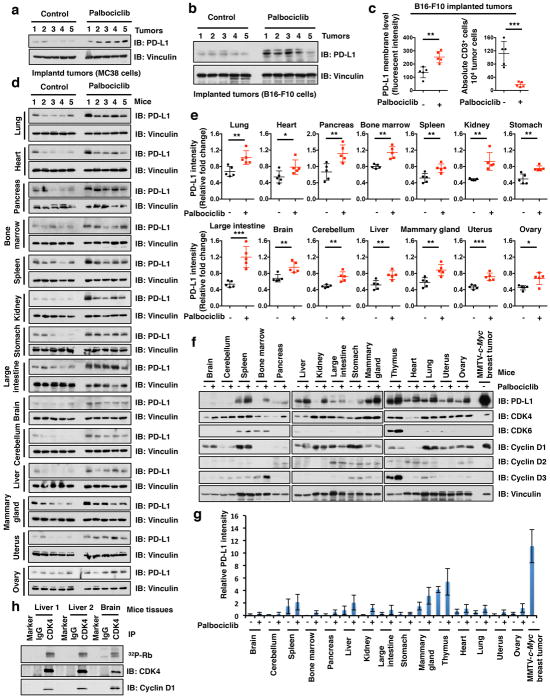
Extended Data Figure 3. CDK4/6 inhibitor, palbociclib, treatment elevated PD-L1 levels in vivo.
a, b, Immunoblot (IB) analysis of whole cell lysates (WCL) derived from MC38 or B16-F10 mouse tumor cell line implanted tumors treated with palbociclib (150 mg/kg body weight, by gastric gavage) or vehicle for 7 days. n = 5 mice per experimental group.
c, FACS analysis for PD-L1 or CD3+ T-cell populations from MC38 implanted tumors treated with vehicle or palbociclib for 7 days. n = 5 mice per experimental group.
d, IB analysis of WCL derived from multiple organs in mice treated with palbociclib (150 mg/kg body weight, by gastric gavage) or vehicle for 7 days. n = 5 mice per experimental group.
e, Quantification of PD-L1 protein bands intensity in Extended Data Fig. 3d by using the ImageJ software. n = 5 mice per experimental group.
f, IB analysis of WCL derived from 15 different tissues with/without palbociclib treatment and MMTV-c-Myc induced breast tumors.
g, Quantification of PD-L1 protein bands intensity in Extended Data Fig. 3f by using the ImageJ software. n = 3 biological replicates
h, In vitro kinase assay for Rb through using immunoprecipitated CDK4/cyclin D kinase complex from liver or brain by anti-CDK4 antibody IP. Note that cyclin D-CDK4 complex in non-dividing organs (livers and brains) displayed kinase activity, which might explain why CDK4/6 inhibitor elevated PD-L1 in these organs. Error bars, ± s.d., two-tailed t-test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.